SNMP TL;DR Takeaways:
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) acts as a communication protocol, collecting data from network devices and conveying it to management systems for efficient network monitoring and troubleshooting.
- SNMP and SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) may share similar acronyms, but they serve distinct purposes. SNMP focuses on network management, while SMTP facilitates email transmission across networks.
- SNMP dances to the tune of UDP (User Datagram Protocol), leveraging its speed and simplicity for efficient data exchange between devices, while incorporating error detection and recovery mechanisms for reliability.
In the vast realm of computer networks, efficient management is crucial for smooth operations and troubleshooting.
This is where Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) steps in as a reliable ally.
SNMP is like the conductor of an orchestra, coordinating and monitoring the performance of network devices. Let’s dive into the world of SNMP, exploring its applications, distinguishing it from SMTP, and uncovering whether it dances to the tune of TCP or UDP.
What is SNMP and How It Is Used?
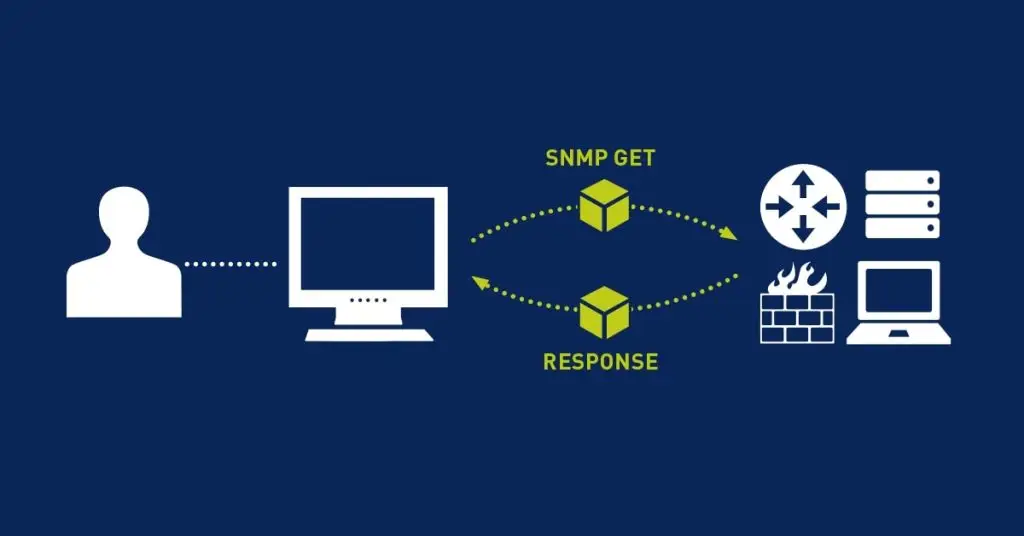
SNMP, the unsung hero of network management, serves as a bridge between network management systems and devices. It ensures a seamless exchange of information by acting as a communication protocol.
The Simple Network Management Protocol tirelessly roams the network landscape, much like a messenger, collecting valuable data from devices and conveying it back to the management system.
SNMP enables administrators to monitor bandwidth usage, detect anomalies, and perform remote configuration changes. It serves as the eyes and ears of the network, providing real-time insights into device performance, error notifications, and configuration details.
By harnessing the power of the Simple Network Management Protocol, administrators can proactively manage their networks, troubleshoot issues efficiently, and ensure optimal performance.
The SNMP architecture consists of three essential components. The managed devices, including routers, switches, and servers, form the actors on the network stage.
Agents, embedded within these devices, act as intermediaries, collecting and forwarding data to the management systems.
Lastly, the network management systems orchestrate the Simple Network Management Protocol symphony, analyzing the received data, generating reports, and issuing commands to the managed devices.
This symbiotic relationship ensures that network administrators have a comprehensive overview of their network’s health and can take informed actions accordingly.
What is the Difference Between SNMP and SMTP?
Though SNMP and SMTP may appear similar due to their acronymic resemblance, they serve distinct purposes in the realm of networking. SNMP focuses on network management, while SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, primarily used for email transmission.
To draw a comparison, let’s imagine SNMP as a diligent janitor, meticulously monitoring and managing the network’s cleanliness and functionality. On the other hand, SMTP resembles a dedicated postman, ensuring the smooth delivery of electronic mail across networks.
While the Simple Network Management Protocol keeps a watchful eye on the network’s health, SMTP ensures that your emails traverse the vast digital landscape, reaching their intended recipients promptly.
Both SNMP and SMTP play vital roles in their respective domains, contributing to efficient management and seamless communication within networks.
Understanding their differences allows network administrators to leverage the right protocol for the task at hand, ensuring smooth operations and reliable information exchange.
Is the Simple Network Management Protocol a TCP or UDP?
In the vast world of networking, protocols dictate the rules of engagement between devices. When it comes to SNMP, it chooses to dance to the tune of UDP (User Datagram Protocol) rather than TCP (Transmission Control Protocol).
UDP, known for its speed and simplicity, can be likened to a quick messenger that delivers messages or “datagrams” between devices without the need to establish a persistent connection.
The Simple Network Management Protocol leverages the connectionless nature of UDP to efficiently transmit information from managed devices to the network management system.
However, this choice comes with trade-offs. UDP lacks built-in error checking and reliability mechanisms present in TCP. But fear not! SNMP compensates for this by incorporating error detection and recovery mechanisms within its protocol design.
It allows to provision of a reliable and efficient method of data exchange while benefiting from the speed and simplicity offered by UDP.
Additional FAQs:
- Q1: Can SNMP be used to manage both wired and wireless networks?
A1: Absolutely! It’s a versatile protocol that can be utilized to manage both wired and wireless networks, offering administrators a unified approach to network management.
- Q2: Are there different versions of SNMP?
A2: Indeed! SNMP has undergone several iterations over the years, with version 3 being the most recent. Each version introduces improvements in security, performance, and functionality.
- Q3: Can SNMP be used to manage non-network devices?
A3: While it’s primarily designed for managing network devices, it can also be extended to manage certain non-network devices, such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and environmental monitoring systems.
Conclusion
In the vast landscape of network management, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) stands tall as a reliable and versatile protocol.
Its ability to monitor and control network devices empowers administrators to maintain optimal network performance and troubleshoot issues efficiently.
So embrace it, unravel its power, and orchestrate your network’s success.

