IPv6 TL;DR Takeaway:
Curious about IPv6?
Discover what it is, how it works, and why you should consider using it.
Also, learn how to configure it and explore its creation and implementation in 2023.
IPv6, the latest version of the Internet Protocol, is a next-generation standard designed to complement and eventually replace IPv4.
Every device connected to the internet, be it a computer, smartphone, IoT sensor, or smart home component, requires a unique numerical IP address to communicate with other devices.
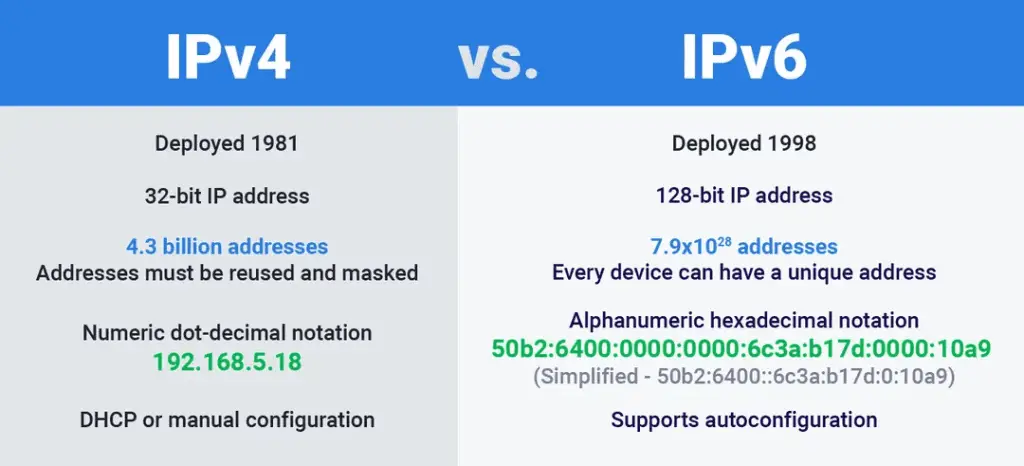
It uses a 128-bit addressing scheme, offering an astronomical number of unique addresses (approximately 340 sextillions) compared to the limited address space of IPv4.
IPv6 works by assigning a unique IP address to each device connected to the internet.
These IP addresses act as digital identifiers, enabling communication and routing of data packets.
Unlike IPv4, which uses 32-bit addressing, IPv6 utilizes 128-bit addressing, allowing for an almost limitless number of unique IP addresses. This vast address space is essential for accommodating the growing number of internet-connected devices in our modern era.
Using IPv6 offers several compelling advantages.
Firstly, it provides a virtually unlimited supply of unique IP addresses, eliminating the need for complex address translation mechanisms like NAT.
Additionally, it offers native support for mobile devices, allowing seamless roaming and improved connectivity.
The protocol also incorporates enhanced autoconfiguration methods, simplifying network setup.
IPv6’s hierarchical routing structure enhances efficiency, reducing the size of routing tables and improving network performance.
Furthermore, it can be augmented with IPsec, offering robust security measures for data transmission.
Configuring IPv6 depends on the operating system and network infrastructure you are using.
Most modern operating systems and network devices come with built-in support.
To enable or disable IPv6, you can typically navigate to the network settings or network adapter properties.
However, it’s important to note that disabling it may limit your ability to access certain online resources that have transitioned to IPv6.
It is generally recommended to keep it enabled to ensure compatibility and future-proof your network.
IPv6 was introduced by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in 1998 as a solution to the impending exhaustion of IPv4 addresses.
The transition to IPv6 has been a gradual process, and as of 2023, its functionality deployment continues.
While IPv4 remains more popular due to compatibility and cost considerations, the industry is steadily moving towards the adoption of IPv6.
The coexistence of both protocols allows for a gradual transition and ensures a smooth evolution of the internet infrastructure.
Q: What happened to IPv5?
A: IPv5, also known as the Internet Stream Protocol, was an experimental protocol designed to support connection-oriented communications for voice and video. However, it shared the same limitation as IPv4 with its 32-bit addressing scheme, which led to the development and adoption of IPv6.
Q: Will IPv4 be completely shut down?
A: There is no official date for the shutdown of IPv4. As IPv6 deployment progresses, the world will gradually move away from IPv4. IPv4 addresses can still be reused, sold, and repurposed during the transition to IPv6, ensuring continued internet access for users.
In the era of expanding connectivity, IPv6 emerges as the solution to address the limitations of IPv4.
Its vast address space, improved security features, and enhanced efficiency make it the protocol of the future. While the transition may take time, the industry is steadily adopting this new standard.
By understanding what it is, how it works, and its advantages, you can prepare yourself for the evolving landscape of internet connectivity and ensure a seamless experience in the digital world.
Embrace its power and unlock the full potential of a connected future.
Thanks to the Ethernet standard, we can count on networks as they are today. It is one of the fundamental standards that allowed millions of devices to communicate with each other.
Its standardizations also contributed to its truly massive adoption.
So, in this guide, you will learn about the PoE (Power over Ethernet) standard, which makes it possible to supply electrical energy to a large number of devices connected to the network, through the same Ethernet network cable through which we pass the data.
Refers to the transmission of electrical power to compatible devices. This is possible through the same network cable that allows connection to local area networks.
This standard has been around since 2003 and was an important change.
It is designed in such a way that it does not impede optimal connectivity and does not reduce performance. This allows users to be able to safely use devices that are compatible with the PoE standard.
As we can see, the network cable has two main functions: data transmission and power supply. Thus we avoid having to use two different ones.
Not all types of PoE are the same. We are going to see which are the main standards that we can use and what general specifications each one has.
The uses, as we will see, also vary from one to another. However, the basis of operation will be the same and will allow the use of a network cable as well so that it can pass power.
Consequently, PoE++ was born, which is subdivided into two types: Type 3 and Type 4.
They are referred to as Type 3 and Type 4 since the earlier PoE and PoE+ standards are also known as Type 1 and Type 2, respectively.
One of the direct objectives of this standard is to eliminate the need to install equipment for power supply.
Consequently, there is a significant saving in the costs of implementing a network.
Likewise, people who are not exactly involved in networks can perceive the advantages of using PoE.
It will be much easier for anyone to know that through a single cable, they are already managing to provide electricity to a device (IoT equipment, for example) and, in turn, connectivity.
In the long run, you will not have to think at all about which cable to disconnect from the current, which is from the network, and which one you should not disconnect.
This is why we’ve enlisted Power over Ethernet (PoE) advantages:
But not everything is perfect. So, we’ve also enlisted Power over Ethernet (PoE) disadvantages: