In the digital age, connectivity is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity. That’s where Network as a Service (NaaS) comes in.
As the number of connected devices continues to skyrocket, we’re entering an era of hyperconnectivity.
This new era is transforming the way we live and work, enabling a level of communication and collaboration that was once unimaginable.
But with this increased connectivity comes complexity.
By adopting a NaaS model, organizations can navigate the complexities of the hyperconnectivity era with ease and efficiency.
Hyperconnectivity is a term that describes the accelerating and expanding interconnectedness of different nodes, systems, and organizations in our digital world.
It’s driven by advancements in technology such as the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, and cloud computing, which enable devices, systems, and people to connect and communicate with each other seamlessly.
In the context of digital transformation, hyperconnectivity plays a crucial role. It enables organizations to break down silos, improve collaboration, and streamline operations.
With hyperconnectivity, data can flow freely across the organization, providing valuable insights that drive decision-making and innovation.
Moreover, hyperconnectivity enables new business models and opportunities.
For instance, it allows organizations to provide more personalized and efficient services to their customers, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
It also enables organizations to leverage data and analytics to identify new market opportunities and make more informed strategic decisions.
In the era of hyperconnectivity, cybersecurity has become a top priority for organizations. Network as a Service (NaaS) plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity by providing a robust and secure network infrastructure.
One of the key ways NaaS enhances cybersecurity is through centralized network management. With NaaS, the entire network is managed and monitored by a single provider.
This centralized approach allows for better visibility and control over the network, making it easier to detect and respond to potential security threats.
NaaS providers also use advanced security technologies and practices to protect the network. These may include encryption, intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and firewalls.
Some NaaS providers also offer security services such as threat intelligence and incident response, further enhancing the organization’s cybersecurity posture.
Moreover, NaaS can help organizations stay compliant with various cybersecurity regulations.
NaaS providers often have expertise in compliance and can ensure that the network meets the necessary standards and regulations.
Network as a Service (NaaS) is a versatile solution that can benefit a wide range of organizations across various sectors.
Here are some use cases:
As we move further into the era of hyperconnectivity, the role of Network as a Service (NaaS) is set to become increasingly important.
With the proliferation of connected devices and the growing demand for reliable, high-speed connectivity, NaaS offers a scalable and flexible solution that can adapt to these changing needs.
One of the key trends shaping the future of NaaS is the integration with cloud services.
As more organizations move their operations to the cloud, NaaS providers are offering cloud-based network services that can be easily scaled up or down depending on the organization’s needs.
This not only provides greater flexibility but also reduces the need for upfront capital investment in network infrastructure.
Another trend is the increasing focus on security. With the rise in cyber threats, NaaS providers are enhancing their security offerings to protect their clients’ networks.
This includes advanced threat detection and response capabilities, as well as compliance management services to help organizations meet their regulatory requirements.
Furthermore, the advent of technologies like 5G and edge computing is set to open up new possibilities for NaaS. These technologies can enable low-latency, high-speed connectivity for a wide range of applications, from autonomous vehicles to remote surgery.
NaaS providers will play a crucial role in enabling these applications by providing the necessary network infrastructure.
With NaaS, businesses can offload the complex task of managing their network infrastructure to a service provider like LayerLogix.
This not only frees up valuable resources but also ensures that the network is managed by experts who can proactively monitor and respond to issues, minimizing downtime and maintaining operational continuity.
Moreover, the scalability of NaaS means that businesses can easily adjust their network capacity to match their needs. This flexibility can lead to significant cost savings, as businesses only pay for what they use.
Furthermore, the enhanced security features of NaaS can protect businesses from cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of their data.
NaaS TL;DR Takeaway
Discover the concept of Network as a Service (NaaS) and how it revolutionizes networking in 2023.
Explore its features, benefits, and challenges, and learn how businesses can leverage this cloud-based model for enhanced flexibility and scalability.
Network as a Service (NaaS) is a cloud service model where organizations rent network services from cloud providers. With NaaS, businesses can operate their networks without the burden of maintaining a dedicated network infrastructure.
Unlike traditional networking approaches that rely on physical hardware, NaaS leverages software-based network functions, enabling companies to create their networks using virtualized resources.
This shift from hardware-centric networking to software-defined NaaS empowers businesses to leverage the scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency of the cloud.
While NaaS shares similarities with Software as a Service (SaaS), they serve different purposes.
SaaS primarily focuses on delivering software applications over the internet, whereas NaaS specifically caters to networking needs.
NaaS provides a comprehensive suite of network services, including routing, security, load balancing, and more, as a cloud-based solution.
By adopting NaaS, businesses can overcome the limitations of traditional network infrastructures, reduce costs, and enhance their operational efficiency.
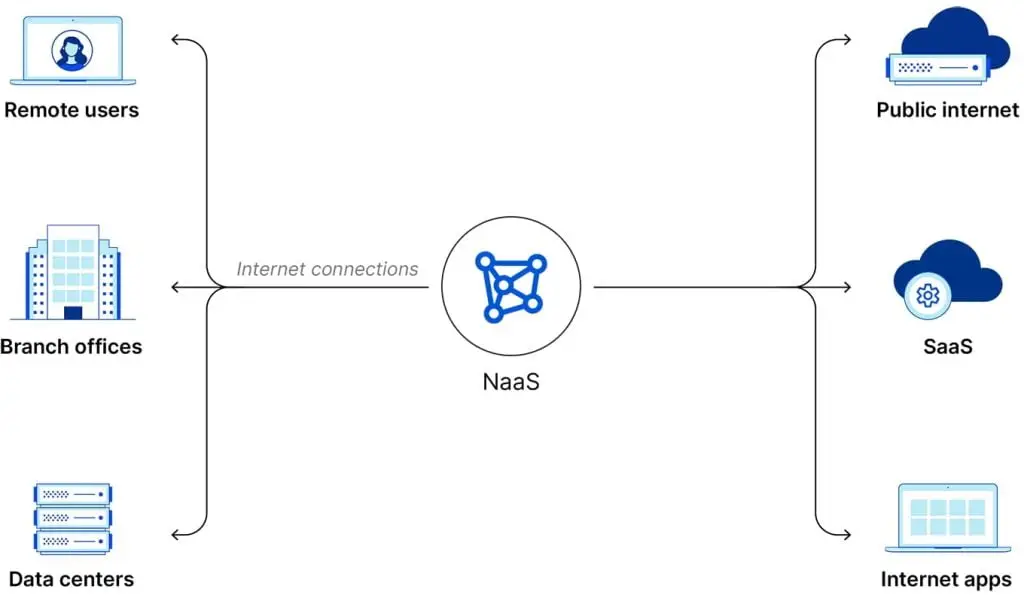
NaaS revolutionizes networking by offering a range of features that empower businesses to optimize their network infrastructure effectively. Here are some key features of NaaS:
Examples of NaaS implementations include virtual private networks (VPNs) that provide secure remote access to company networks, cloud-based firewalls that protect against unauthorized access, and load balancers that distribute network traffic efficiently.
By leveraging NaaS, businesses can deploy these services quickly and cost-effectively while offloading the maintenance and management responsibilities to the service provider.
NaaS offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive networking solution for businesses. Let’s explore some key advantages:
Despite the numerous benefits, there are some challenges associated with NaaS adoption: