In the digital age, email remains one of the primary forms of communication for individuals and businesses alike. With the convenience and speed of email comes the significant risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. Email encryption is a critical tool in safeguarding sensitive information transmitted and stored via email. This article delves into the importance of email encryption, the risks associated with unencrypted emails, the implications of poor email inbox etiquette, and how compromised email and account protections can lead to data theft. We will also explore real-world scenarios of email breaches and highlight best practices for email encryption and cybersecurity.
Email encryption is the process of encoding email messages to protect them from unauthorized access. Only the intended recipient, who has the decryption key, can read the encrypted message. The importance of email encryption cannot be overstated, particularly when dealing with sensitive data such as personal information, financial details, and confidential business communications.
Sensitive data should always be transmitted securely and protected while at rest. Encryption ensures that data remains confidential during transmission and storage.
When sending emails with sensitive data, using secure transmission protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) is essential. TLS encrypts the data during transmission, protecting it from interception by malicious actors.
Data at rest refers to information that is stored on a device or server. Encrypting data at rest ensures that even if a device is compromised, the data remains protected and inaccessible without the decryption key.
Poor email inbox etiquette can lead to several security vulnerabilities, including increased risk of phishing attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Email and account protections can be compromised through various methods, including phishing, malware, and brute force attacks. Understanding these methods is crucial for implementing effective defenses.
Phishing involves sending fraudulent emails that appear legitimate to trick recipients into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details. These emails often contain malicious links or attachments.
Malware, such as keyloggers and spyware, can be installed on a user’s device through malicious email attachments or links. Once installed, malware can capture sensitive information and send it to the attacker.
Brute force attacks involve attempting numerous password combinations to gain access to an account. Weak passwords are particularly vulnerable to such attacks.
In 2020, a major financial institution fell victim to a targeted phishing attack. The attackers sent emails to employees, masquerading as internal IT support, requesting login credentials for a routine security update. Several employees fell for the scam, providing their login details. The attackers then used these credentials to access the institution’s network, stealing sensitive financial data and customer information.
A healthcare provider experienced a data breach when an employee clicked on a malicious link in an email, inadvertently installing spyware on their computer. The spyware captured login credentials and provided the attackers access to the provider’s database, resulting in the theft of patient records and confidential medical information.
A manufacturing company was targeted by a competitor through a brute force attack on the CEO’s email account. The attackers successfully cracked the password and accessed sensitive emails containing proprietary designs and business strategies. The breach resulted in significant financial losses and competitive disadvantages for the company.
Encryption serves as a robust defense mechanism against unauthorized access to sensitive information. By encrypting emails and data, organizations can protect their communications from interception and ensure that only authorized recipients can access the information.
The healthcare industry is one of the most targeted sectors for cyber-attacks due to the high value of medical records on the black market. Implementing email encryption in healthcare organizations is crucial to protect patient data and comply with regulations such as HIPAA.
Ensure that emails are encrypted using strong protocols, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and TLS, to protect data during transmission and at rest.
Require multi-factor authentication for accessing email accounts. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors.
Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees on identifying phishing emails and practicing good email security habits.
Encourage the use of strong, unique passwords for email accounts and mandate regular password updates to minimize the risk of brute force attacks.
Implement monitoring and auditing tools to detect suspicious email activities and potential security breaches in real-time.
Ensure that sensitive attachments are encrypted before being sent via email to protect the data from unauthorized access.
Email encryption is an essential strategy for protecting sensitive information and maintaining the security of communications. By understanding the importance of encryption, recognizing the risks associated with poor email practices, and implementing robust security measures, organizations can safeguard their data and build a strong defense against cyber threats. Adopting best practices such as using strong encryption protocols, implementing multi-factor authentication, and educating employees on security awareness will help ensure that email communications remain secure and confidential.
By focusing on these areas, organizations can create a secure email environment, protect sensitive information, and comply with data protection regulations. The healthcare industry, in particular, can benefit significantly from implementing these best practices to protect patient data and maintain trust.
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity is far more than a buzzword—it’s an essential safeguard that protects businesses from the chaos of cyber threats. Understanding the importance of cybersecurity services for businesses and enterprises is crucial, especially as IT services and Managed Service Providers (MSPs) play a pivotal role in this ever-evolving digital battlefield.
Picture a world where cybersecurity is as casually treated as leaving the office coffee pot on over the weekend. Come Monday, instead of the aroma of burnt coffee, the office is met with the smoldering remains of a once-secure network. This is the reality for businesses that neglect cybersecurity. It’s akin to playing a game of digital Russian roulette, where the stakes are not just data but the very essence of the business itself.
In this whimsical analogy, imagine the chaos as employees scramble to recover from the digital devastation. The finance department is in shambles, trying to piece together missing financial records. The HR department is in disarray, with sensitive employee information potentially compromised. Clients are in an uproar, questioning the integrity and reliability of the company. This dramatic scene underscores a crucial point: cybersecurity is not a luxury but a necessity. Just as businesses wouldn’t leave their physical premises unsecured, they cannot afford to leave their digital assets unprotected. The humor here serves to highlight a serious message—complacency in cybersecurity can lead to catastrophic consequences.
The digital landscape is filled with cautionary tales of companies that underestimated cyber threats. Consider the infamous data exposure at Pegasus Airlines, where a simple cloud misconfiguration led to the exposure of personally identifiable information (PII) and jeopardized the safety of passengers and crew. This incident wasn’t merely a technical glitch; it was a failure of monumental proportions that highlighted the critical importance of proper cybersecurity protocols and vigilant oversight. The aftermath saw a significant loss of customer trust, legal repercussions, and a damaged reputation that took years to rebuild.
Then there’s the colossal breach at Yahoo, where 3 billion accounts were compromised, shaking the internet giant to its core. This breach wasn’t just about stolen passwords—it revealed the inner workings of countless personal lives and businesses, causing widespread panic and distrust. Yahoo’s failure to protect its users’ data resulted in a loss of user confidence and a drastic decline in its market value. These are not mere stories—they are stark reminders of the fragility of digital trust and the devastating impact of cybersecurity failures. They serve as powerful case studies that emphasize the necessity of robust cybersecurity measures and proactive strategies to prevent such breaches.
IT services and MSPs are the vigilant sentinels in the cybersecurity narrative. They design defense mechanisms and act as first responders when digital alarms go off. Their role goes beyond implementing security measures; they cultivate a culture of cybersecurity awareness and resilience. These professionals continuously monitor networks, update systems, and respond to emerging threats, ensuring that businesses remain secure in an increasingly hostile digital environment.
Their importance cannot be overstated. In the same way that firefighters are crucial in preventing and responding to fires, IT services and MSPs are indispensable in preventing and mitigating cyber threats. They must convince the C-suite that investing in cybersecurity is a strategic move, akin to investing in the very foundation of the business. This involves not only deploying advanced security technologies but also educating employees about best practices and potential threats. By fostering a proactive cybersecurity culture, IT services and MSPs help businesses build a resilient defense against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Cybersecurity is multifaceted, encompassing everything from technical encryption intricacies to combating social engineering tactics. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution but a bespoke suit tailored to each business’s unique needs. Often, the weakest link in the chain is not the technology but the human behind the screen. This is why a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy includes not only technological defenses but also training and awareness programs for employees.
Consider encryption, a fundamental component of cybersecurity. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. However, this technical safeguard must be complemented by measures to prevent social engineering attacks, where cybercriminals manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information. Training employees to recognize phishing emails, suspicious links, and other common tactics is essential in creating a robust cybersecurity defense. Additionally, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to sensitive information. By addressing both the technological and human elements of cybersecurity, businesses can create a comprehensive defense strategy that is resilient against a wide range of threats.
To persuade businesses and enterprises of the importance of cybersecurity services, appealing to both logic and emotions is essential. It involves painting a picture of a future where cybersecurity seamlessly integrates into business operations, not as a hindrance but as an enabler of positive possibilities. This creative approach can include storytelling, real-world examples, and even humorous analogies to make the message more relatable and engaging.
For instance, imagine a scenario where a business successfully thwarts a major cyber attack due to its robust cybersecurity measures. The relief and gratitude of the employees, the trust and loyalty of the clients, and the enhanced reputation of the company all contribute to a compelling narrative that underscores the value of investing in cybersecurity. By highlighting the tangible benefits of cybersecurity, such as protecting sensitive data, maintaining customer trust, and ensuring business continuity, businesses can see cybersecurity as a strategic asset rather than a mere expense. This creative persuasion helps shift the perception of cybersecurity from a necessary evil to a valuable investment that drives long-term success and stability.
In conclusion, cybersecurity services are not just accessories; they are the armor businesses need to venture into the digital battlefield. IT services and MSPs must wield the sword of satire to cut through complacency and champion cybersecurity. In the grand theater of business, cybersecurity is not just a role—it’s the script that ensures the show goes on.
By adopting a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, businesses can protect themselves from the ever-present threat of cyber attacks. This includes investing in advanced technologies, educating employees, and fostering a culture of vigilance and resilience. As businesses navigate the complexities of the digital world, cybersecurity will continue to play a critical role in safeguarding their success and ensuring their longevity. The time to act is now—before the next cyber threat strikes, leaving businesses scrambling to pick up the pieces.
The manufacturing industry is in the crosshairs of cybercriminals.
As manufacturing businesses embrace digital transformation and interconnected systems, they become vulnerable to increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Ignoring these threats is not an option; it’s a recipe for disaster. This guide unveils the essential cybersecurity practices that every manufacturing leader, from the C-suite to IT professionals, needs to know to safeguard their operations, protect sensitive data, and ensure business continuity.
Imagine this: Jennifer, the COO of a thriving manufacturing business, is staring at a screen full of flashing red alerts.
Her worst nightmare – a cyberattack – has brought their entire operation to a grinding halt.
Production lines are down, sensitive data is being held hostage, and the financial losses are ticking upwards like a runaway timer.
In fact, as per CIT-net, the manufacturing industry is a prime target, experiencing a staggering 23% of all security incursions worldwide. This makes manufacturing a particularly vulnerable sector, more than any other industry in the world.
And the cost? Data-Guard365 estimates the average data breach sets manufacturers back a whopping $1 million.
But it gets worse: CIT-net also reports that manufacturers face an average cost of $2 million to restore operational systems after a successful ransomware attack, significantly higher than the global average of $812,360.
This highlights the crippling financial impact of cyberattacks specifically on manufacturing operations.
Think of cybersecurity as the immune system of your business – it’s not just about protecting against threats but ensuring the overall health and resilience of your operations.
Ready to learn how to build an impenetrable cybersecurity fortress around your manufacturing business?
Sadly, these threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and aggressive.
It’s not just about hackers trying to steal your lunch money anymore; it’s about disrupting entire operations and causing significant financial and reputational damage.
Ransomware attacks are like something out of a Hollywood thriller – hackers seize control of your critical systems and data, holding them hostage until you cough up a hefty ransom.
And trust me, you don’t want to be on the receiving end of one of these attacks.
CIT-net reports that a chilling 23% of all corporate ransomware attacks specifically target manufacturing companies. That’s like having a giant target painted on your back.
Ever clicked on a link that seemed a little fishy?
That’s phishing – a sneaky tactic where cybercriminals disguise themselves as trustworthy entities to trick you into revealing sensitive information like passwords or financial data.
It’s like leaving your front door wide open with a sign inviting malicious agents to come in.
Sometimes, the most significant threat comes from within. Insider threats – whether intentional or accidental – can be just as damaging as external attacks.
Data-Guard365 found that a shocking 70% of breaches in manufacturing stem from internal vulnerabilities, primarily due to human error. That’s why educating your employees about cybersecurity best practices is non-negotiable.
And it’s not just these three… the manufacturing industry is also grappling with the rise of IoT (Internet of Things), which opens up a whole new can of worms.
But also according to Data-Guard365, with the integration of IoT, security incidents have increased by a worrying 30%.
Let’s roll up our sleeves and dive into the next section where we’ll explore essential cybersecurity practices for manufacturers.
Okay, so we’ve explored the treacherous landscape of cybersecurity threats.
Now, let’s equip ourselves with the tools and strategies to fortify our defenses and build an impenetrable fortress around our manufacturing businesses.
By implementing these essential cybersecurity practices, manufacturing businesses can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.
Now, how about we add some real-world credibility to these practices?
We’ve all heard those horror stories – the ransomware attacks, the data breaches, the crippling downtime. But what about the companies that bounced back stronger than ever?
The ones who turned those cybersecurity setbacks into resounding triumphs?
Let’s delve into some real-world examples and see how they used those “actionable steps” to fortify their defenses and emerge as shining examples of cybersecurity resilience:
Last year (2023), Clorox suffered a $356 million wake-up call. It highlighted the importance of swift incident response and robust supply chain security.
Imagine if Clorox had partnered with Layer Logix before the attack:
Norsk Hydro’s decision to fight back against ransomware was commendable, but the $70 million price tag underscores the importance of proactive security measures.
Imagine if Norsk Hydro had taken a preventative approach with Layer Logix:
Applied Materials $250 million loss exposed the vulnerability of even tech giants to supply chain attacks.
Now, envision a scenario where Applied Materials, with Layer Logix as their cybersecurity partner, took a proactive stance:
In 2017, Mondelez International stared down the barrel of the devastating NotPetya malware attack, resulting in a staggering $100 million loss.
But what if Mondelez had been equipped with Layer Logix’s expertise?
JBS, a global meat processing giant, felt the sting of ransomware in 2021, forking over $11 million to regain control of their systems.
However, imagine a world where JBS partnered with Layer Logix:
Bridgestone Americas’ encounter with the LockBit ransomware gang in 2022 highlighted the importance of data protection and swift recovery in the face of an attack.
With Layer Logix on their side, Bridgestone could have:
Johnson Controls’ 2023 tango with the notorious Dark Angels ransomware gang led to a hefty $27 million remediation bill.
However, partnering with Layer Logix could have rewritten their story:
These cases underscore that cybersecurity is an ongoing journey, not a destination.
By embracing a proactive approach, partnering with cybersecurity experts like Layer Logix, and learning from the experiences of others, manufacturing companies can turn potential setbacks into opportunities for growth and resilience.
Reading about these cybersecurity nightmares might have you reaching for the panic button, but there’s good news: You don’t have to face the digital battlefield alone.
Partner with Layer Logix, the cybersecurity experts who turn those scary stories into success stories.
We’re not just another IT company; we’re your dedicated allies in the fight against cybercrime, offering:
Don’t wait for a cybersecurity disaster to strike before taking action.
Visit Layer Logix’s dedicated Manufacturing Services page today to learn more about how we can help you build an impenetrable fortress around your manufacturing business.
Contact Layer Logix today and let’s start building a safer, more secure future for your manufacturing business.
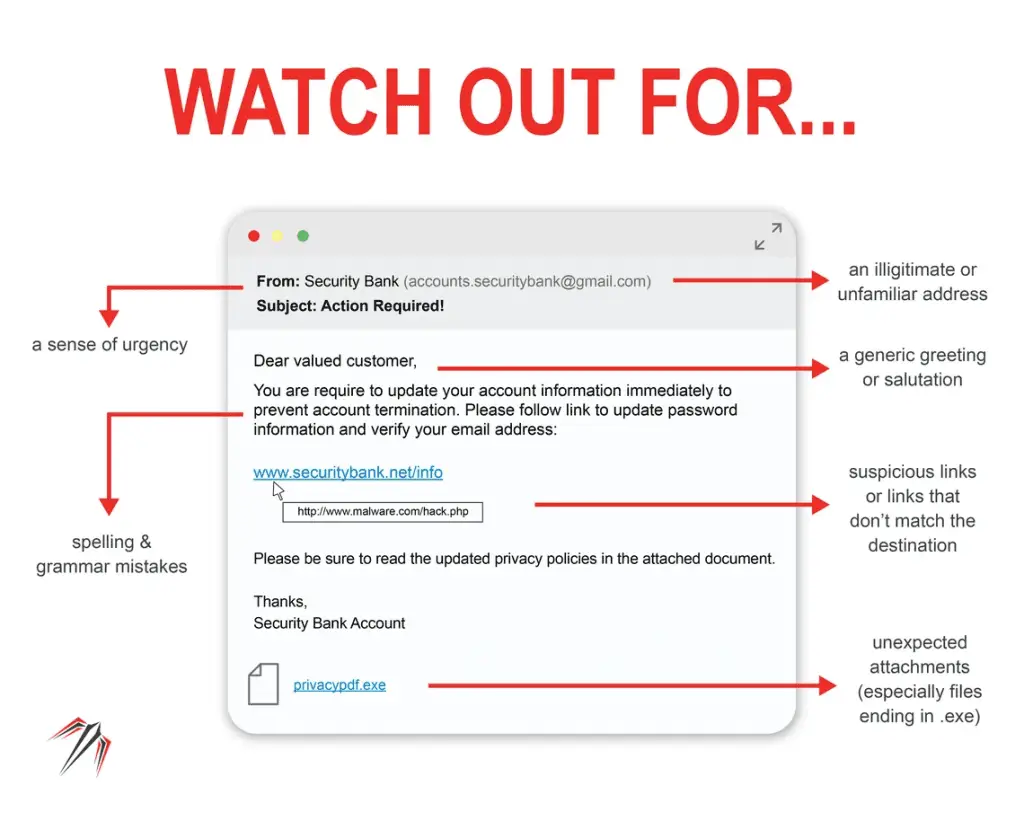
Cybercriminals are constantly devising new tactics to create and send dangerous email attachments, using them as a gateway to unleash malware, viruses, and other malicious software.
To safeguard ourselves and our systems, it’s essential to understand why some email attachments are dangerous, which types pose a high risk, and how to spot them effectively.
In this article, we will delve into the world of dangerous email attachments and equip you with the knowledge to protect yourself.
Email attachments pose a threat primarily because they can contain malicious files or code that can exploit vulnerabilities in our systems.
Cybercriminals leverage social engineering techniques to trick recipients into opening these attachments, often disguising them as harmless or enticing files.
Once opened, these attachments can unleash malware, viruses, ransomware, or other harmful software, leading to data breaches, system damage, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Among the high-risk email attachments, executables (.exe) are particularly dangerous.
These files have the capability to run codes that can modify a computer system.
Cybercriminals often disguise them with innocent-sounding names to deceive recipients into opening them.
Executable files can be vehicles for ransomware, encrypting files and demanding payment for decryption, or they can serve as carriers for other malicious software.
Such as .js, .vbs, .php, or .asp files, are another high-risk attachment type. While not inherently malicious, cybercriminals utilize scripts to install malware on victims’ computers.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in software or manipulating user interactions, malicious scripts can execute harmful commands or actions, compromising system integrity and privacy.
In various formats (.doc, .xls, .ppt, .pdf) also pose a significant risk. Cybercriminals inject malicious code into seemingly harmless documents, such as Microsoft Office files or PDFs, and prompt users to enable macros or click on phishing links.
Enabling macros or interacting with these documents can lead to the activation of malware, unauthorized access, or theft of login credentials.

Archive files, including .zip, .rar, or .7z, are commonly used by cybercriminals to conceal malware. These compressed files provide an effective means of delivering malicious executables, scripts, or infected documents.
By enticing recipients with intriguing filenames or exploiting their curiosity, cybercriminals trick users into extracting the contents of the archive, inadvertently activating the hidden malware.
Disk image files, such as .iso, .img, or .dmg, are particularly risky, especially for macOS users. These files can contain executables, scripts, or documents that can compromise system security.
Cybercriminals often bundle disk images with seemingly harmless files, using social engineering to entice users into executing the installer and unknowingly installing malware.

Not all email attachments are dangerous, but it’s essential to exercise caution and verify the authenticity of the attachment and the sender before opening it.
Cybercriminals often use social engineering tactics to trick users into opening malicious attachments, so it’s crucial to be vigilant.
If you receive a suspicious email attachment, it’s best to avoid opening it.
Delete the email and attachment immediately.
If the email appears to be from someone you know, contact them through another communication channel to verify the attachment’s legitimacy.
While email attachments from trusted sources are generally safer, it’s still essential to exercise caution.
Cybercriminals can compromise email accounts or use spoofing techniques to make an email appear legitimate.
Always verify the sender and the content of the attachment before opening it.
Antivirus software is an essential layer of protection, but it’s not foolproof.
Cybercriminals constantly develop new techniques to evade detection.
Therefore, it’s crucial to adopt a multi-layered security approach, which includes being vigilant, staying informed, and following best practices for email safety.