Cybercriminals are constantly devising new tactics to create and send dangerous email attachments, using them as a gateway to unleash malware, viruses, and other malicious software.
To safeguard ourselves and our systems, it’s essential to understand why some email attachments are dangerous, which types pose a high risk, and how to spot them effectively.
In this article, we will delve into the world of dangerous email attachments and equip you with the knowledge to protect yourself.
Why Are Some Email Attachments Dangerous and Which Are High Risk?
Email attachments pose a threat primarily because they can contain malicious files or code that can exploit vulnerabilities in our systems.
Cybercriminals leverage social engineering techniques to trick recipients into opening these attachments, often disguising them as harmless or enticing files.
Once opened, these attachments can unleash malware, viruses, ransomware, or other harmful software, leading to data breaches, system damage, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
1) Executables
Among the high-risk email attachments, executables (.exe) are particularly dangerous.
These files have the capability to run codes that can modify a computer system.
Cybercriminals often disguise them with innocent-sounding names to deceive recipients into opening them.
Executable files can be vehicles for ransomware, encrypting files and demanding payment for decryption, or they can serve as carriers for other malicious software.
2) Scripts
Such as .js, .vbs, .php, or .asp files, are another high-risk attachment type. While not inherently malicious, cybercriminals utilize scripts to install malware on victims’ computers.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in software or manipulating user interactions, malicious scripts can execute harmful commands or actions, compromising system integrity and privacy.
3) Documents
In various formats (.doc, .xls, .ppt, .pdf) also pose a significant risk. Cybercriminals inject malicious code into seemingly harmless documents, such as Microsoft Office files or PDFs, and prompt users to enable macros or click on phishing links.
Enabling macros or interacting with these documents can lead to the activation of malware, unauthorized access, or theft of login credentials.

4) Archive Files
Archive files, including .zip, .rar, or .7z, are commonly used by cybercriminals to conceal malware. These compressed files provide an effective means of delivering malicious executables, scripts, or infected documents.
By enticing recipients with intriguing filenames or exploiting their curiosity, cybercriminals trick users into extracting the contents of the archive, inadvertently activating the hidden malware.
5) Disk Image Files
Disk image files, such as .iso, .img, or .dmg, are particularly risky, especially for macOS users. These files can contain executables, scripts, or documents that can compromise system security.
Cybercriminals often bundle disk images with seemingly harmless files, using social engineering to entice users into executing the installer and unknowingly installing malware.

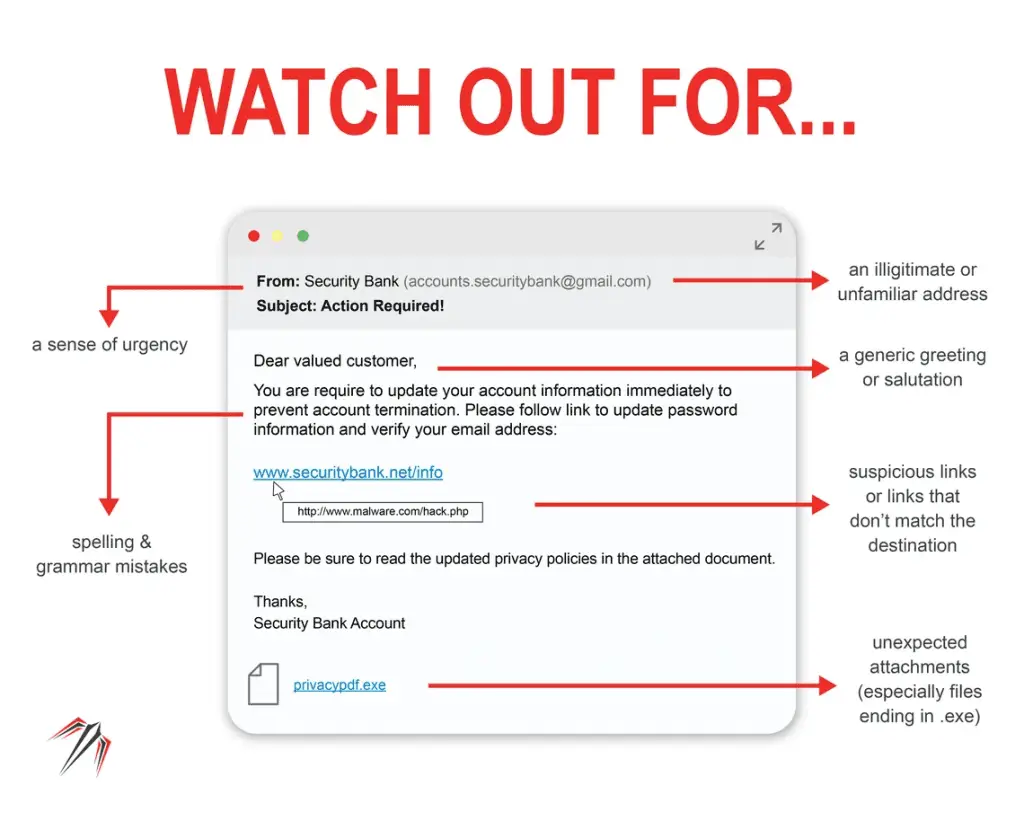
Tips to Spot Dangerous Email Attachments
- Be skeptical: Maintain a healthy level of skepticism when it comes to email attachments. Question the authenticity and relevance of the attachment before opening it. If something seems suspicious or out of the ordinary, it’s better to err on the side of caution.
- Verify the sender: Check the sender’s email address and ensure it matches the expected sender. Pay attention to any misspellings, unfamiliar addresses, or suspicious domains. If you have doubts about the sender’s identity, contact them through alternative means to verify the attachment’s legitimacy.
- Scan attachments: Utilize reputable antivirus software to scan email attachments before opening them. This can help detect and eliminate potential threats before they can harm your system.
- Avoid enabling macros: Exercise caution when enabling macros in documents, especially if they come from unknown or untrusted sources. Disable macros by default and only enable them if you trust the source and the content of the document.
- Keep software up to date: Regularly update your operating system and applications to ensure you have the latest security patches. This can help mitigate vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit through malicious email attachments.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the latest email scams and malware trends. By educating yourself and staying updated on cybersecurity best practices, you can better recognize and avoid dangerous email attachments.
Additional FAQs
Can all email attachments be dangerous?
Not all email attachments are dangerous, but it’s essential to exercise caution and verify the authenticity of the attachment and the sender before opening it.
Cybercriminals often use social engineering tactics to trick users into opening malicious attachments, so it’s crucial to be vigilant.
What should I do if I receive a suspicious email attachment?
If you receive a suspicious email attachment, it’s best to avoid opening it.
Delete the email and attachment immediately.
If the email appears to be from someone you know, contact them through another communication channel to verify the attachment’s legitimacy.
Are email attachments from trusted sources always safe?
While email attachments from trusted sources are generally safer, it’s still essential to exercise caution.
Cybercriminals can compromise email accounts or use spoofing techniques to make an email appear legitimate.
Always verify the sender and the content of the attachment before opening it.
Should I rely on antivirus software to detect dangerous email attachments?
Antivirus software is an essential layer of protection, but it’s not foolproof.
Cybercriminals constantly develop new techniques to evade detection.
Therefore, it’s crucial to adopt a multi-layered security approach, which includes being vigilant, staying informed, and following best practices for email safety.

