Enter microsegmentation, an innovative approach to network security that is revolutionizing the way organizations protect their sensitive data and resources.
In this article, we delve into the world of micro-segmentation, exploring its significance, benefits, challenges, and real-world examples.
Find out how it can potentially reduce costs and explore steps to get started with this advanced security approach.
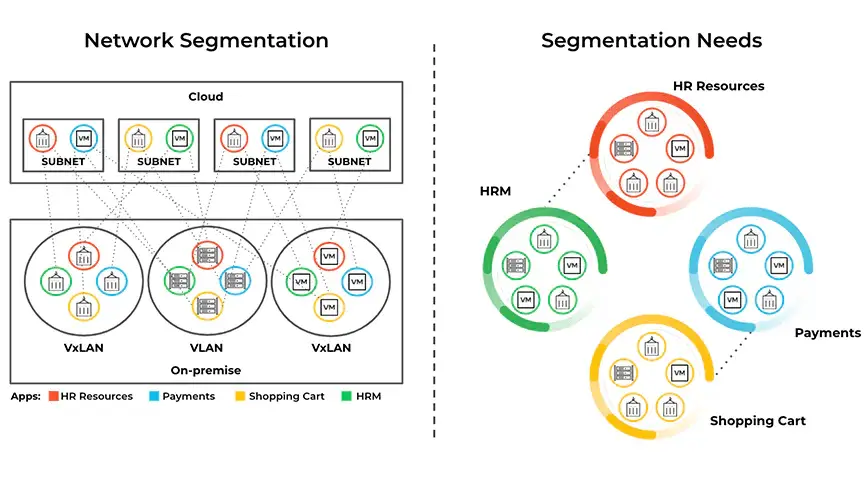
Microsegmentation in networking refers to the practice of dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments, or microsegments, to enhance security and control network traffic.
Unlike traditional network security measures that rely on perimeter defenses, micro-segmentation operates at a granular level within the network, allowing organizations to establish fine-grained access controls and contain potential security breaches.
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, micro segmentation has become increasingly important. It provides organizations with a proactive security approach that goes beyond the traditional defense-in-depth strategy.
By implementing micro segmentation, organizations can limit the lateral movement of attackers within their network, preventing them from freely accessing sensitive data or systems.
This approach reduces the attack surface, making it significantly harder for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and carry out successful attacks.
Micro-segmentation also plays a vital role in protecting critical assets and meeting regulatory compliance requirements.
By segmenting the network and applying specific security policies to each segment, organizations can ensure that only authorized individuals or devices have access to sensitive data or resources.
This level of control helps organizations maintain compliance with industry regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Microsegmentation offers a range of benefits that significantly enhance an organization’s security posture. Let’s delve into some of the key advantages, as well as the challenges and examples in practice.
While micro segmentation offers numerous benefits, implementing and managing it does come with some challenges. These include:
Many organizations across various industries have successfully implemented micro segmentation to strengthen their security posture. For example:
Microsegmentation is not only a robust security strategy but can also have a positive impact on an organization’s cost efficiency.
Let’s explore how microsegmentation can reduce costs while enhancing network security.
Firstly, microsegmentation improves resource utilization by enabling organizations to allocate their network resources more efficiently.
By segmenting the network, organizations can allocate specific resources, such as bandwidth, processing power, and storage, to each segment based on its unique requirements.
This targeted resource allocation ensures that resources are not wasted on unnecessary or unused segments, leading to cost savings.
Additionally, microsegmentation minimizes the risk of a security breach or data breach, which can result in substantial financial losses.
By implementing granular access controls and isolating sensitive data or critical systems, organizations reduce the potential impact and cost of a breach.
The containment provided by microsegmentation restricts lateral movement and limits an attacker’s ability to move freely within the network, minimizing the potential damage caused by a successful breach.
Furthermore, microsegmentation helps organizations achieve compliance with regulatory standards. Non-compliance can lead to severe financial penalties, legal consequences, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
By implementing microsegmentation and enforcing specific security policies for each segment, organizations can meet the regulatory requirements relevant to their industry. Compliance with these standards avoids costly penalties and ensures that the organization maintains a positive reputation.
While microsegmentation itself may involve upfront costs, such as implementing the necessary infrastructure and deploying appropriate security solutions, the long-term cost savings and risk reduction outweigh the initial investment.
The proactive nature of microsegmentation helps organizations avoid the substantial costs associated with remediation, legal fees, loss of customer trust, and potential fines resulting from a security breach.
Getting started with microsegmentation requires a systematic approach to ensure successful implementation and maximize its benefits.
Here are some essential steps to consider when embarking on a microsegmentation journey:
By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement microsegmentation and reap its benefits, including enhanced security, reduced risk, and improved network control.
There are many users who, despite having full knowledge and operation of computer networks, still ignore the differences between a hub, a switch, or a router.
All of these are hardware devices that make it possible to connect computers to networks, which means that you will surely have to turn to a technician for any problem.
If that is your case, then we advise you that the LayerLogix professional team is ready to support you with any questions and related problems.
That is why in this post we will explain what the true function of a hub, a switch, or a router is, and which one to use in each scenario, hoping to save you headaches.
The hub is a device that has the function of interconnecting the computers of a local network. Its operation is simpler than the switch and the router since the hub receives data from one computer and transmits it to the others.
The Hub links computers within the same local network, therefore if any of the computers sends a message, the hub will take care of replicating this message in all the computers within this local network.
At the time this occurs, no other switch can send a signal. Its release comes after the previous signal has been completely distributed.
In a hub, it is possible to have several ports (entrances to connect the network cables of each computer).
Generally, there are hubs with 8, 16, 24, and 32 ports, but the number varies depending on the model and manufacturer of the device.
If the cable of a machine is disconnected or has a defect, the network does not stop working.
Currently, hubs are being replaced by switches, due to the small cost difference between the two.
Now, the switch is a very similar device to the hub, but with the difference that the data coming from the source, the computer is only sent to the destination computer.
This is because switches create a kind of exclusive communication channel between source and destination. In this way, the network is not “limited” to a single computer in sending information.
This increases network performance since communication is always available, except when two or more computers try to send data simultaneously to the same machine.
This feature also reduces errors (data packet collisions, for example). Just like the hub, a switch has several ports and the number varies in the same way.
Last, but not least… The router is a device used in larger networks.
It is more “intelligent” than the switch, since, in addition to fulfilling the same function, it also has the best route that a given data packet must follow to reach its destination.
It is as if the network were a big city and the router chooses the shortest and least congested path. Hence the name router.
The Router is responsible for sending data packets between different networks, they can be LAN or WAN networks, fulfilling the same functions as a Switch or a Hub, only not limited to a local network.
These Routers incorporate firewalls that protect the local network against possible attacks or dangers.
In short, these are the basic functions that Switch, Hubs, and Routers have.
They are devices that can sometimes be confused but have different functionalities and capabilities. And it could be said that the most important is the router since it is key in our day to day to connect.