As we forge ahead into 2024, the digital landscape is rich in challenges and opportunities. The cybersecurity domain, in particular, is a space where businesses must constantly adapt to safeguard their assets.
With cyberattacks projected to cost the global economy over $10.5 trillion annually by the end of this year, the stakes have never been higher.
The advent of generative AI has given rise to deepfakes—sophisticated forgeries that can deceive even the most discerning eyes and ears. These AI-generated deceptions are not just a threat to individual privacy but also a weapon against corporate security. As phishing scams become more convincing, they pave the way for unprecedented business email compromise (BEC), virtual kidnappings, and other scams.
Leaders in cybersecurity technology like LayerLogix are responding with innovative solutions designed to detect and neutralize such threats. Their security fabric scrutinizes web traffic for anomalies and provides zero-day threat protection—a necessity in this new era of cyber deception.
Ransomware attacks have evolved from mere data encryption to double extortion tactics. Cybercriminals now threaten to leak sensitive information if their demands are not met, adding an additional layer of coercion.
To counteract these threats, businesses must implement comprehensive backup solutions, cultivate a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees, and employ sophisticated threat intelligence systems.
With an increasing number of businesses relying on cloud services, vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure have become prime targets for attackers. Similarly, supply chain compromises represent a growing concern as attackers exploit trusted relationships between vendors and clients.
In response, organizations are turning towards zero-trust frameworks that enforce strict access controls and continuous verification protocols—ensuring that only authenticated users can access sensitive data.
Zero-day exploits remain a significant challenge as they exploit unknown vulnerabilities before developers have a chance to address them. APTs pose an even greater risk due to their stealthy nature and potential for long-term damage.
Businesses must invest in robust vulnerability management programs that include regular software updates, patch management processes, and advanced endpoint protection technologies capable of detecting subtle signs of intrusion.
Despite its use by cyber adversaries, AI is also revolutionizing cybersecurity defense mechanisms. Automated systems powered by AI can outperform human capabilities when it comes to detecting complex threats in real-time.
Smart authentication methods bolster security measures further by ensuring only legitimate users gain access while automated incident response protocols rapidly contain breaches should they occur.
The dynamic field of cybersecurity demands that businesses remain vigilant at all times. By staying up-to-date with trends such as deepfakes, ransomware evolution, cloud vulnerabilities, zero-day exploits, and APTs—and embracing AI-driven defenses—companies can navigate through these turbulent waters with confidence.
LayerLogix stands at the forefront of this fight against cybercrime with our cutting-edge managed IT services tailored specifically for your business’s data privacy needs. Visit our blog or engage with our expert team today; let us help you build an impregnable digital fortress around your valuable assets in 2024 and beyond.
Remember: In the realm of cybersecurity services—the best defense is not just a good offense but an informed one too!
Why do computers always know what time it is? How do they agree at the same time? Network Time Protocol (NTP) is responsible for that.
Developed in 1981 by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware, this protocol is mostly used for synchronizing clocks of computer systems over networks with variable latency.
But not only that. There’s more to the Network Time Protocol or NTP for short.
Network Time Protocol TL;DR Takeaway
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a protocol for synchronizing clocks of computer systems over networks with variable latency. NTP uses a hierarchical structure of time servers and clients to distribute accurate time information across the network.
NTP consists of four main components:
The Network Time Protocol uses a request-response communication pattern between clients and servers. A client sends a request packet to a server, containing its timestamp.
The server receives the request packet and adds its timestamp. Then sends a response packet back to the client, containing both timestamps.
The client receives the response packet and adds its timestamp again.
Using these four timestamps, the client can calculate two important values:
The Network Time Protocol uses an algorithm called Marzullo’s algorithm to select the most accurate time server from multiple sources. It can also use an extension mechanism called Autokey to provide authentication and encryption for secure communication.

Network Time Protocol (NTP) has many benefits and challenges for network users and administrators. Some of the benefits are:
Some of the challenges are:
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs and threats of network time synchronization. Some of the possible trends and developments for NTP in 2023 are:
Client-Server Network TL;DR Takeaway
Have you ever wondered how web browsers can access web pages from different websites? Or how email clients send and receive messages from different email servers? That’s all thanks to Client-server networks.
The Client-server network is one of the most popular and widely used network models in the world.
It enables many users to share and access resources and applications on the network.
It also provides security, scalability, and reliability for the network.
Want to know more about it? Then keep reading, because we’ll answer further questions.
A Client-server network is a network model that partitions the tasks or workloads between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and the requesters of a resource or service, called clients.
Clients and servers can be separate hardware devices or software programs.
Clients and servers do also communicate over a network using a common protocol.
A protocol is a set of rules and formats that define how data is exchanged between devices or programs.
For example, HTTP is a protocol that defines how web browsers and web servers communicate.
Clients initiate communication sessions with servers, which wait for incoming requests.
Clients send requests to servers, and servers send responses back to clients.
This exchange of messages is an example of a request-response communication pattern.
For example, when you type a web address in your browser, your browser sends a request to the web server that hosts the website, and the web server sends back the web page as a response.
Clients and servers can perform different functions depending on the type of service they provide or request. Some of the common types of client-server services are:

Client-server network has many advantages and disadvantages compared to other network models.
For example, it provides better Security, Scalability, and Reliability than other network models because servers can actually access resources and applications on the network, as well as handle multiple requests from multiple clients, and backup data to recover from failures. But it also has disadvantages, such as:
Cloud Security Access Brokers TL;DR Takeaway
The cloud is awesome, but it’s not perfect. This is where Cloud Security Access Brokers or CASBs for short, come in.
In this article, we will explain what CASBs are, how they work, what they can do, and why you need them for cloud security in 2023.
CASB stands for Cloud Access Security Broker. It’s a fancy name for a security solution that acts as a broker between you and your cloud service providers.
A CASB sits between you and the cloud, monitoring and controlling the traffic that goes back and forth.
CASBs can cover different types of cloud services, such as software-as-a-service (SaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS).
They can also extend the reach of your existing on-premises security infrastructure to the cloud and create new policies for cloud-specific contexts.
CASBs work by intercepting the traffic between you and the cloud services, either through proxies or APIs. After all, Proxies are agents that sit between you and the cloud services, inspecting and modifying the traffic in real-time.
APIs are interfaces that allow CASBs to communicate with cloud services, retrieving and analyzing data and events.
CASBs can perform various functions depending on the type of traffic they intercept and the policies they enforce. Some of the common functions of CASBs are:
CASBs are not just security solutions. They are also business enablers. They allow you to use the cloud without compromising your security or compliance. They enable you to:
CASBs are not just nice to have. They are essential for cloud security in 2023. Here are some of the reasons why you need CASBs for cloud security in 2023:
SOC-as-a-Service (SOCaaS) TL;DR Takeaway:
Let me tell you a brief story about SOC-as-a-Service (SOCaaS).
A story about you and your online business.
You have a website that attracts millions of visitors, a mobile app that delights your customers, and a cloud platform that powers your operations. You’re living the dream, right?
Wrong. You’re living in a nightmare. A nightmare where cybercriminals are lurking in the shadows, waiting for the right moment to strike. They want to steal your data, disrupt your services, extort your money, and ruin your reputation.
They have the tools, the skills, and the motivation to do it. So, how can you stop them?
In this article, we’ll tell you the “how”: everything you need to know about SOC-as-a-Service.
A security operations center (SOC) is a centralized hub that acts as the brain and nerve center of your cybersecurity. A SOC consists of security analysts, engineers, tools, processes, and policies that work together to protect your organization from cyberattacks.
But building and maintaining an in-house SOC can be a huge hassle for many organizations. You need to invest in hardware, software, staff training, recruitment, retention, compliance, and updates.
You also need to deal with alert fatigue, skills shortage, evolving threats, and limited visibility.
That’s where SOC-as-a-Service comes in. SOCaaS is a service that outsources your security operations to a third-party provider that operates and maintains a fully-managed SOC on your behalf.
You simply pay a monthly or annual fee based on your needs and usage.
With SOCaaS, you get access to a team of experienced security professionals who monitor your environment 24/7 using state-of-the-art tools and techniques.
They can detect and respond to threats faster and more effectively than you could on your own.
They can also provide you with reports, insights, recommendations, and best practices to improve your security posture.
SOCaaS means that you don’t have to worry about the technical details of security operations.
You can focus on your core business while trusting that your security is in good hands.
SOC services include a range of capabilities that cover the entire spectrum of security operations.
Let me break them down for you:
You need SOC services because they can help you achieve the following benefits:

MDR stands for managed detection and response, which is a subset of SOCaaS that focuses on detecting and responding to threats. SOCaaS provides a broader range of services that cover prevention, analysis, reporting, compliance, and more.
MSSP stands for managed security service provider, which is a generic term for any provider that offers outsourced security services. SOCaaS is a specific type of MSSP that offers a fully-managed SOC as a service.
There are several factors to consider when choosing a SOCaaS provider, such as:
If any of these situations resonate with you, then you might be interested in Testing-as-a-Service or TaaS:
Let’s say you are a software developer who wants to deliver top-notch products to your customers. You know that testing is a vital part of the development process, but you also face some hurdles.
Maybe you don’t have enough time, resources, or skills to test your software in-house.
Maybe you want to avoid biases and conflicts of interest that could skew the testing results.
Maybe you want to cut costs and speed up the testing execution. Or maybe you just want to focus on your core competencies and leave the testing to the experts.
That’s why we wrote today’s article.
TaaS stands for Testing-as-a-Service. It is a service delivery model that enables you to outsource your testing activities to a third-party provider who has the expertise, tools, and infrastructure to perform various types of testing for your software products and services.
You can access their testing tools and environments on a pay-per-use or subscription basis.
You can also hire testers who can perform manual or automated testing for you.
The process of using Testing-as-a-Service may vary depending on the provider and the type of testing you need, but it generally involves four steps:

TaaS offers many benefits for software developers who want to improve their testing processes and outcomes. Some of these benefits are:
However, Testing-as-a-Service also comes with some challenges that you need to be aware of before using it. Some of these challenges are:
TaaS is not a one-size-fits-all solution. There are different types of TaaS that you can choose from depending on your testing needs and goals.
Some of the common types of TaaS are:
These are just some examples of the types of TaaS that you can use for your software products and services.
There may be other types of TaaS that are more suitable for your specific needs and preferences.
Personal Area Network TL;DR Takeaway
Do you know how do wireless devices interact with each other? This is all thanks to Personal Area Networks or PAN for short.
But let’s not spoil this article for you. Keep reading to find out more about them and how they function.
Personal Area Network (PAN) is a network model that connects electronic devices within a user’s immediate area. PAN can be used for various purposes, such as:
A protocol is a set of rules and formats that define how data is exchanged between devices or programs.
For example, Bluetooth is a protocol that defines how wireless devices communicate.
Therefore, PAN consists of two main components:

PAN uses different communication patterns depending on the type of connection and protocol. Some of the common communication patterns are:
Personal Area Network (PAN) has many advantages and disadvantages for network users and administrators. Some of the advantages are:
Some of the disadvantages are:
Personal Area Network (PAN) is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs and trends of network users and technologies.
Some of the possible trends and developments for PAN in 2023 are:
Understanding the meaning and differences between IOC vs. IOA is crucial in cybersecurity.
While they may sound similar, they serve distinct purposes in identifying potential threats and fortifying cybersecurity defenses.
Let’s explore their definitions, their significance in identifying threats, and how they play different roles in strengthening cybersecurity measures.
Indicators of Compromise (IOC) form the forensic evidence that suggests a system has been breached or compromised. They act as telltale artifacts, scattered across various sources such as log files, network traffic, and system memory.
Examples of IOCs include IP addresses, domain names, file hashes, and patterns of behavior.
These nuggets of evidence allow security researchers and professionals to detect known malicious activities like malware infections, phishing attempts, and ransomware attacks.
IOCs are instrumental in uncovering common attack methods, such as brute-force attacks and SQL injections.
Through collaboration and information sharing within the cybersecurity community, security teams can detect and mitigate threats more effectively.

Indicators of Attack (IOA) reveal the intentions and techniques employed by threat actors during a cyberattack.
Unlike IOCs that focus on specific artifacts, IOAs are concerned with patterns of behavior and the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems.
IOAs are proactive, and capable of identifying potential threats before they inflict significant damage.
By analyzing unusual network traffic, suspicious account activities, and unauthorized system changes, organizations can detect IOAs and take immediate action to prevent attacks.
IOAs also enable the identification of emerging threats and facilitate the adjustment of security strategies to counteract them effectively.

While both IOCs and IOAs are crucial components in incident response and threat intelligence, they have fundamental differences in their nature and application:
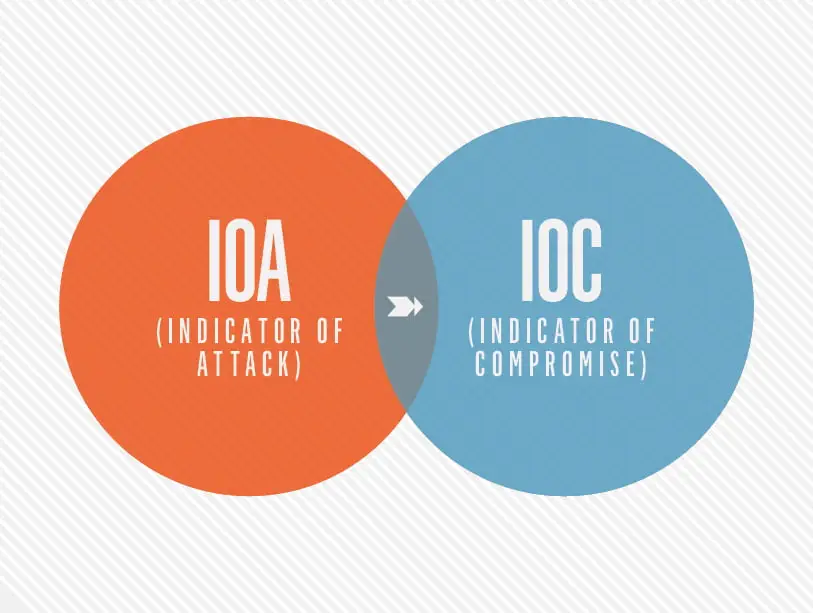
IOCs are artifacts that suggest a system has already been breached, whereas IOAs are dynamic behavioral patterns indicating an ongoing or impending attack.
IOCs are reactive, providing insights into known malicious activities. In contrast, IOAs take a proactive approach by identifying attack tactics, techniques, and procedures.
IOCs are based on known malicious activities and serve as evidence of compromise, while IOAs revolve around understanding the attacker’s motivations and strategies.
IOCs offer static signatures that can be used to defend against future attacks, while IOAs monitor evolving attacker movements and aim to detect their activity in real time.
IOCs are typically detected after a compromise has occurred, allowing security teams to respond, contain, and remediate the threat.
IOAs, on the other hand, provide early indications of an attack, enabling organizations to implement proactive measures to intercept and prevent the attack before it leads to a data breach or significant damage.
By comprehending these differences, organizations can leverage the strengths of both IOC and IOA approaches to strengthen their cybersecurity posture, detect threats on time, and minimize the impact of potential breaches.
Embracing a holistic cybersecurity strategy that leverages IOC vs. IOA ensures a proactive and dynamic response to the ever-evolving threat landscape, thereby safeguarding critical data and preserving digital trust.
IOCs provide evidence of compromise, enabling the detection and remediation of known malicious activities.
IOAs, on the other hand, offer proactive insights into attack behaviors, facilitating the interception and prevention of cyber attacks.
By harnessing the strengths of both approaches, organizations can establish a robust defense posture and mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats.
Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay secure.
Enter microsegmentation, an innovative approach to network security that is revolutionizing the way organizations protect their sensitive data and resources.
In this article, we delve into the world of micro-segmentation, exploring its significance, benefits, challenges, and real-world examples.
Find out how it can potentially reduce costs and explore steps to get started with this advanced security approach.
Microsegmentation in networking refers to the practice of dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments, or microsegments, to enhance security and control network traffic.
Unlike traditional network security measures that rely on perimeter defenses, micro-segmentation operates at a granular level within the network, allowing organizations to establish fine-grained access controls and contain potential security breaches.
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, micro segmentation has become increasingly important. It provides organizations with a proactive security approach that goes beyond the traditional defense-in-depth strategy.
By implementing micro segmentation, organizations can limit the lateral movement of attackers within their network, preventing them from freely accessing sensitive data or systems.
This approach reduces the attack surface, making it significantly harder for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and carry out successful attacks.
Micro-segmentation also plays a vital role in protecting critical assets and meeting regulatory compliance requirements.
By segmenting the network and applying specific security policies to each segment, organizations can ensure that only authorized individuals or devices have access to sensitive data or resources.
This level of control helps organizations maintain compliance with industry regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
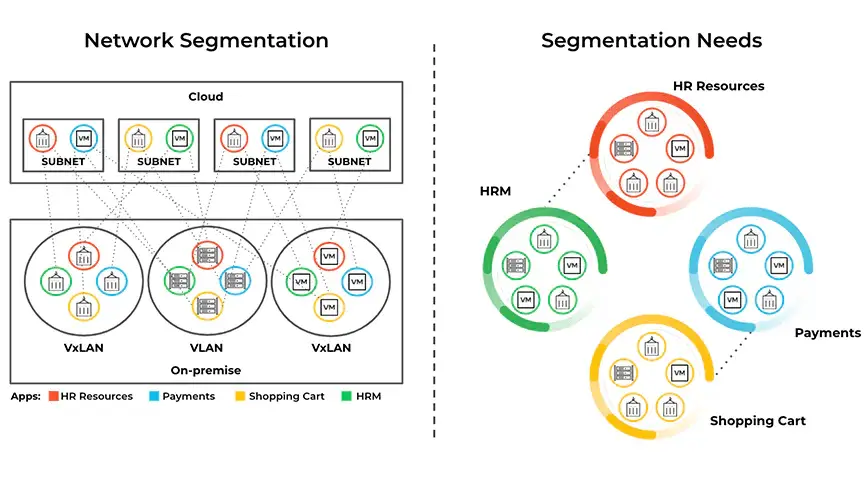
Microsegmentation offers a range of benefits that significantly enhance an organization’s security posture. Let’s delve into some of the key advantages, as well as the challenges and examples in practice.
While micro segmentation offers numerous benefits, implementing and managing it does come with some challenges. These include:
Many organizations across various industries have successfully implemented micro segmentation to strengthen their security posture. For example:
Microsegmentation is not only a robust security strategy but can also have a positive impact on an organization’s cost efficiency.
Let’s explore how microsegmentation can reduce costs while enhancing network security.
Firstly, microsegmentation improves resource utilization by enabling organizations to allocate their network resources more efficiently.
By segmenting the network, organizations can allocate specific resources, such as bandwidth, processing power, and storage, to each segment based on its unique requirements.
This targeted resource allocation ensures that resources are not wasted on unnecessary or unused segments, leading to cost savings.
Additionally, microsegmentation minimizes the risk of a security breach or data breach, which can result in substantial financial losses.
By implementing granular access controls and isolating sensitive data or critical systems, organizations reduce the potential impact and cost of a breach.
The containment provided by microsegmentation restricts lateral movement and limits an attacker’s ability to move freely within the network, minimizing the potential damage caused by a successful breach.
Furthermore, microsegmentation helps organizations achieve compliance with regulatory standards. Non-compliance can lead to severe financial penalties, legal consequences, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
By implementing microsegmentation and enforcing specific security policies for each segment, organizations can meet the regulatory requirements relevant to their industry. Compliance with these standards avoids costly penalties and ensures that the organization maintains a positive reputation.
While microsegmentation itself may involve upfront costs, such as implementing the necessary infrastructure and deploying appropriate security solutions, the long-term cost savings and risk reduction outweigh the initial investment.
The proactive nature of microsegmentation helps organizations avoid the substantial costs associated with remediation, legal fees, loss of customer trust, and potential fines resulting from a security breach.
Getting started with microsegmentation requires a systematic approach to ensure successful implementation and maximize its benefits.
Here are some essential steps to consider when embarking on a microsegmentation journey:
By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement microsegmentation and reap its benefits, including enhanced security, reduced risk, and improved network control.
Explore the world of Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) and discover how this cutting-edge technology revolutionizes data centers.
This innovative approach combines computing, storage, and networking resources into a single, cohesive “building block.” With its software-defined nature, it brings unparalleled flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability to modern IT infrastructures.
Learn about the differences between converged and hyper-converged systems, as well as the relationship between HCI and virtualization.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) represents a revolutionary shift in the design and management of data center infrastructure.
It is an all-in-one solution that seamlessly integrates computing, storage, and networking resources, eliminating the need for separate hardware components.
By adopting a Software-Defined Everything approach, it harnesses the power of virtualization and intelligent software to deliver unified management, improved resiliency, and simplified scalability.
HCI leverages Software-Defined Storage (SDS) to control storage at the operating system or hypervisor layer.
This eliminates the reliance on proprietary storage hardware, reducing costs and enhancing flexibility.
The virtual storage controllers running on each node within the cluster ensure unified storage management, resiliency, and failover capabilities.
Similarly, Software-Defined Networking (SDN) provides a centralized interface for administrators to manage network traffic and distribute resources efficiently.
The beauty of itI lies in its ability to automate the provisioning and configuration of the entire networking stack. Abstracting the underlying hardware, it enables IT teams to allocate resources quickly, scale as needed, and respond to changing demands with ease.
This level of automation improves IT infrastructure efficiency, freeing up valuable time and resources for businesses to focus on innovation and service delivery.

In 2023, HCI continues to evolve, shaping the future of data center architecture.
The core concept behind it is the unification of the data center stack elements into an abstracted layer of available IT resources.
By converging server hardware with direct-attached storage media, it leverages virtualization to create a single resource pool that can be distributed as needed.
Gone are the days of dealing with the complexities and limitations of traditional infrastructure.
Embraces commodity hardware, allowing organizations to build their infrastructure using readily available resources.
This approach offers unparalleled scalability, performance, and resilience. Every ounce of hardware potential is utilized without leaks, overhead, or bottlenecks, enabling businesses to optimize their IT investments.
The virtualized resources within the HCI environment become a unified pool, easily managed and allocated through the relevant software.
Administrators can dynamically provision and scale resources to match the changing workload demands, optimizing performance and enhancing user experience.
The integration of Software-Defined Storage (SDS) in HCI eliminates the need for proprietary storage hardware.
The virtual storage controllers distribute and manage data across the HCI cluster, ensuring data redundancy, fault tolerance, and efficient utilization of available storage.
In the event of a hardware failure, the data is automatically shifted to alternative nodes, maintaining data integrity and availability.
With SDN, organizations can adapt to changing network demands, prioritize critical workloads, and ensure seamless connectivity across the HCI infrastructure.
While converged infrastructure (CI) also combines compute, storage, and networking resources, it falls short in comparison to hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) in terms of simplicity, scalability, and management.
However, the components in a converged infrastructure are managed separately, often requiring dedicated applications and administrative teams for each aspect.
This fragmented management approach adds complexity and increases maintenance costs.
In contrast, HCI eliminates the need for separate management interfaces and dedicated teams. With HCI, all resources are managed through a unified interface, streamlining operations and reducing administrative overhead.
The consolidation of hardware and software in HCI results in a smaller footprint, providing greater flexibility for scaling and optimizing resources.
Additionally, converged infrastructure tends to involve a significant hardware footprint, occupying unnecessary space and limiting scalability options.
HCI, on the other hand, leverages software-defined technologies to abstract the hardware layer, enabling organizations to utilize commodity hardware and scale their infrastructure seamlessly.
HCI and virtualization share a close relationship, but they are not synonymous.
Virtualization is the foundation on which HCI is built. It abstracts the underlying hardware and enables the pooling and allocation of resources, providing the basis for HCI’s unified infrastructure.
Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server, optimizing resource utilization and increasing flexibility.
It separates the software from the hardware, enabling the creation of virtualized environments that can be easily managed and scaled.
HCI, on the other hand, eliminates the need for separate storage and networking hardware, allowing organizations to build their infrastructure using commodity hardware and achieve greater efficiency and scalability.
While virtualization focuses on abstracting the hardware layer, HCI encompasses a broader scope by converging the entire data center stack.
By leveraging software-defined storage and networking, HCI simplifies infrastructure management, automates provisioning, and enhances resiliency.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) continues to redefine how organizations design, deploy, and manage their IT infrastructures.
By eliminating the complexities of traditional infrastructure, HCI empowers businesses to achieve greater efficiency, scalability, and agility.
As the data center landscape evolves, HCI stands as a beacon of innovation, enabling organizations to unlock the true potential of their IT investments.
Establishing effective governance policies for Office 365 is crucial to ensure the platform is used securely and competently. The first step in creating these policies is to identify the key stakeholders responsible for overseeing the use of Office 365 within the organization. These stakeholders should establish clear guidelines for accessing and sharing data and define roles and responsibilities for managing security and compliance risks.
It is essential to establish policies that are specific to your organization’s needs. For example, you should restrict certain users from accessing sensitive data or limit file-sharing permissions. Additionally, regular audits should be conducted to ensure compliance with established policies. Training employees on these policies should also be a priority. This will help ensure that all users understand their responsibilities when using Office 365 and can contribute to maintaining a secure environment.
Effective governance and risk management practices are essential for organizations using Office 365. Mitigating risks through robust risk management practices is crucial to ensure data security and regulation compliance. The first step in mitigating risks is identifying threats and vulnerabilities, including internal and external factors. This can be achieved through conducting regular risk assessments. Once identified, appropriate controls should be implemented to minimize the likelihood of an incident.
These controls can include policies, procedures, and technical solutions such as encryption or multi-factor authentication.
Regularly monitoring these controls is also essential to ensure they are practical and up-to-date. Additionally, staff training on security protocols and best practices can help reduce the risk of human error leading to a security breach.
By implementing robust risk management practices, organizations can minimize the potential impact of security incidents on their operations, reputation, and finances while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Ensuring comprehensive security measures for Office 365 is crucial for any organization to safeguard its data and information. With the increasing amount of cyber threats, it is essential to have a multi-layered approach to security. This involves implementing security controls at different levels, such as network security, identity and access management, data encryption, and threat protection. It is essential to clearly understand the security features provided by Office 365 and customize them according to the organization’s needs.
This includes setting up strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, monitoring user activity logs, and defining access policies. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing can help identify potential weaknesses in the system that can be addressed proactively. Educating employees about safe browsing practices and phishing attacks can also reduce the risk of data breaches caused by human error. Organizations can ensure comprehensive security for their Office 365 environment by implementing these measures.
Maintaining strong governance, risk management, and security in Office 365 requires a holistic approach that involves people, processes, and technology. One of the best practices is establishing clear policies and procedures that define the roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders, such as administrators, users, and auditors. These policies should cover data classification, access control, retention, and incident response.
Another best practice is monitoring the environment for potential risks and vulnerabilities using tools such as threat intelligence feeds and security analytics. It’s also essential to stay up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates from Microsoft. Additionally, user education and awareness training can help reduce the risk of human error or malicious activity. Finally, it’s critical to have a robust backup and recovery strategy to ensure business continuity in case of a disaster or cyber attack.
As organizations increasingly move to the cloud, securing cloud-based systems becomes vital to maintaining data privacy and integrity. Office 365 is one such system that requires security hardening to ensure that it remains secure against evolving threats. Security hardening involves implementing various security measures to reduce vulnerabilities and improve the overall security posture of an organization’s Office 365 environment.
This subtopic will explore the importance of Office 365 security hardening, its benefits, and the steps organizations can take to enhance their Office 365 security posture.
Understanding the threat landscape for Office 365 is crucial to ensuring its security. Cybercriminals constantly evolve tactics, techniques, and procedures to exploit vulnerabilities in cloud-based platforms like Office 365. Threats such as phishing attacks, malware infections, and account takeovers are some of the most common methods attackers use. Moreover, with the increasing use of remote workforces and mobile devices, the risk of data breaches has also risen significantly.
Therefore, organizations need to comprehensively understand the threat landscape and implement appropriate security measures to protect their Office 365 environment from potential cyber threats.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a crucial step toward enhancing the security of Office 365. It adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide two or more forms of authentication, such as a password and a verification code sent to their phone or email. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if the password is compromised. MFA can be easily enabled for all users in Office 365 through the admin center, and various factors can be selected based on organizational needs.
Implementing MFA should be a top priority for all organizations to secure their Office 365 environment.
Regularly reviewing and updating security policies is essential in ensuring the continued protection of your Office 365 environment. Security policies should be reviewed periodically to assess their effectiveness and identify potential vulnerabilities. Updates should address any new threats or changes in business processes. This includes updating access control policies, implementing multi-factor authentication, reviewing data retention and deletion policies, and conducting regular employee security awareness training.
By regularly reviewing and updating security policies, organizations can proactively identify and mitigate risks before they become a problem.
Office 365 security hardening is crucial for organizations to protect their sensitive data and prevent cyber attacks. By implementing measures such as multi-factor authentication, data loss prevention, and encryption, businesses can significantly improve their security posture on the platform. However, as cyber threats continue to evolve, it is essential for organizations to stay up-to-date with the latest security features and best practices provided by Microsoft.
Future advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning may also significantly strengthen Office 365 security. Businesses must remain vigilant and proactive in protecting their digital assets.
Cybercriminals are constantly devising new tactics to create and send dangerous email attachments, using them as a gateway to unleash malware, viruses, and other malicious software.
To safeguard ourselves and our systems, it’s essential to understand why some email attachments are dangerous, which types pose a high risk, and how to spot them effectively.
In this article, we will delve into the world of dangerous email attachments and equip you with the knowledge to protect yourself.
Email attachments pose a threat primarily because they can contain malicious files or code that can exploit vulnerabilities in our systems.
Cybercriminals leverage social engineering techniques to trick recipients into opening these attachments, often disguising them as harmless or enticing files.
Once opened, these attachments can unleash malware, viruses, ransomware, or other harmful software, leading to data breaches, system damage, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Among the high-risk email attachments, executables (.exe) are particularly dangerous.
These files have the capability to run codes that can modify a computer system.
Cybercriminals often disguise them with innocent-sounding names to deceive recipients into opening them.
Executable files can be vehicles for ransomware, encrypting files and demanding payment for decryption, or they can serve as carriers for other malicious software.
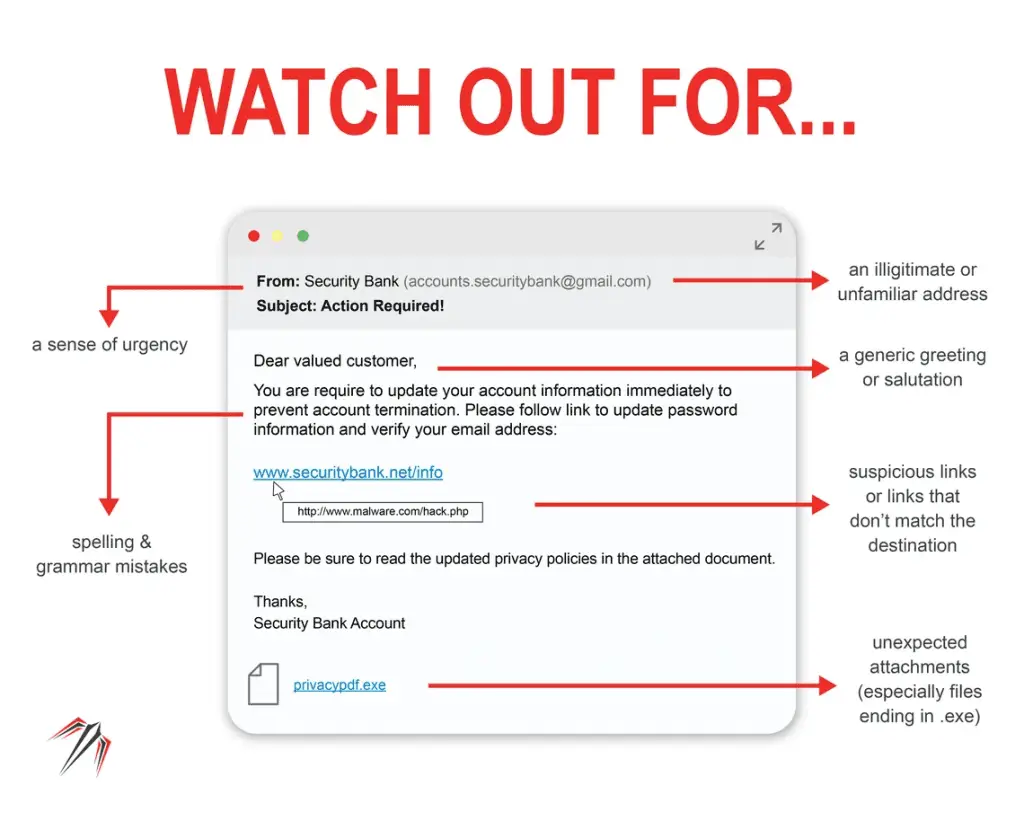
Such as .js, .vbs, .php, or .asp files, are another high-risk attachment type. While not inherently malicious, cybercriminals utilize scripts to install malware on victims’ computers.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in software or manipulating user interactions, malicious scripts can execute harmful commands or actions, compromising system integrity and privacy.
In various formats (.doc, .xls, .ppt, .pdf) also pose a significant risk. Cybercriminals inject malicious code into seemingly harmless documents, such as Microsoft Office files or PDFs, and prompt users to enable macros or click on phishing links.
Enabling macros or interacting with these documents can lead to the activation of malware, unauthorized access, or theft of login credentials.

Archive files, including .zip, .rar, or .7z, are commonly used by cybercriminals to conceal malware. These compressed files provide an effective means of delivering malicious executables, scripts, or infected documents.
By enticing recipients with intriguing filenames or exploiting their curiosity, cybercriminals trick users into extracting the contents of the archive, inadvertently activating the hidden malware.
Disk image files, such as .iso, .img, or .dmg, are particularly risky, especially for macOS users. These files can contain executables, scripts, or documents that can compromise system security.
Cybercriminals often bundle disk images with seemingly harmless files, using social engineering to entice users into executing the installer and unknowingly installing malware.

Not all email attachments are dangerous, but it’s essential to exercise caution and verify the authenticity of the attachment and the sender before opening it.
Cybercriminals often use social engineering tactics to trick users into opening malicious attachments, so it’s crucial to be vigilant.
If you receive a suspicious email attachment, it’s best to avoid opening it.
Delete the email and attachment immediately.
If the email appears to be from someone you know, contact them through another communication channel to verify the attachment’s legitimacy.
While email attachments from trusted sources are generally safer, it’s still essential to exercise caution.
Cybercriminals can compromise email accounts or use spoofing techniques to make an email appear legitimate.
Always verify the sender and the content of the attachment before opening it.
Antivirus software is an essential layer of protection, but it’s not foolproof.
Cybercriminals constantly develop new techniques to evade detection.
Therefore, it’s crucial to adopt a multi-layered security approach, which includes being vigilant, staying informed, and following best practices for email safety.
Discover the ins and outs of XML injection attacks. This comprehensive article covers everything you need to know about XML injection vulnerabilities, their methodologies, and their prevention strategies.
Stay ahead of the curve and protect your systems from this malicious exploit.
Picture this: You’re in a virtual car driving along the information superhighway, minding your own business. Suddenly, an XML injection attack ambushes you like a cunning digital highwayman, aiming to manipulate and exploit your trusty XML files.
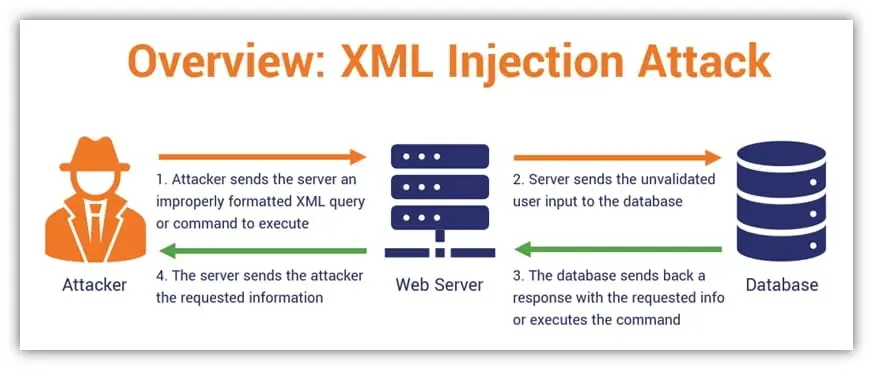
An XML injection vulnerability occurs when an attacker inserts malicious code into XML inputs, intending to disrupt the normal functionality of an application or gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
When an application does not properly validate and sanitize user-supplied XML inputs, it becomes susceptible to these kinds of attacks.
These attacks can target various areas within the XML structure, such as element values, attributes, or namespaces.
By injecting specially crafted XML payloads, attackers can deceive the application into executing unintended actions or exposing confidential information.
To illustrate the severity of an XML injection attack, let’s consider an example.
Imagine an online shopping application that uses XML to store product details.
If an attacker successfully injects malicious XML code, they could manipulate the XML tags, alter product prices, or even modify the entire structure of the XML document.
This could lead to incorrect pricing displayed to customers, unauthorized discounts applied, or even the exposure of sensitive customer data.
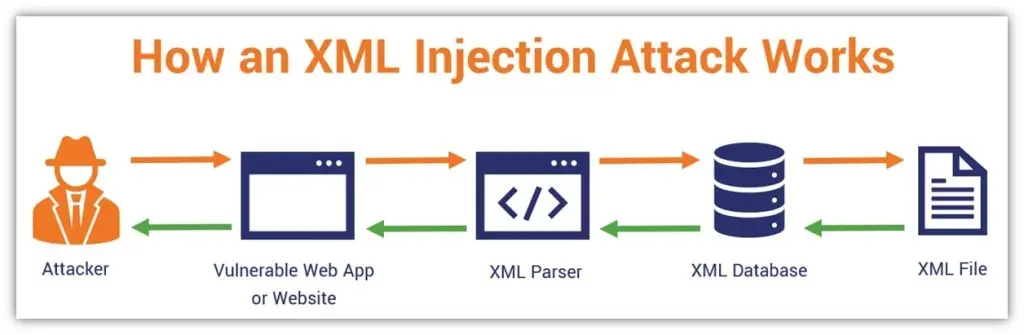
Let’s now peek behind the curtain and explore the methodology employed by XML injection attackers:
While XML injection and SQL injection share some similarities in terms of the potential risks they pose to web applications, they differ in their focus and exploitation techniques.
Let’s explore the key distinctions between these two formidable adversaries:
It revolves around manipulating XML inputs. Attackers leverage vulnerabilities in XML parsing and processing mechanisms to inject malicious code into XML files.
By exploiting these weaknesses, they can modify the XML structure, deceive the application, and execute unintended actions.
On the other hand, SQL injection targets web applications that utilize SQL databases.
Attackers manipulate user inputs to inject SQL queries or fragments into database queries.
These nefarious queries can tamper with database operations, extract sensitive information, or even modify the database structure.
While both attacks can lead to severe consequences, they require different techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. This threat focuses on crafting malicious XML payloads, while SQL injection relies on manipulating SQL queries through specially crafted input.
Now that you’re equipped with knowledge about these attacks, it’s time to steer clear of trouble.
Here are some effective prevention strategies to keep the XML injection highwayman at bay:
Remember, vigilance is the key to a secure digital journey. Stay informed, adopt best practices, and keep your guard up to protect your systems from the stealthy menace of XML injection attacks.
MSI errors 2503 and 2502 are common installation errors that occur during the process of installing or uninstalling software on Windows operating systems. These errors usually indicate that the installer is unable to complete its task due to a problem with permissions or file access. Error 2503 occurs when there is a problem with the installer’s permissions, while error 2502 is related to file access issues.
Various factors, including corrupted files, outdated software, or insufficient user privileges can cause both of these errors. To solve these errors, users can try several troubleshooting steps such as running the installer as an administrator, disabling antivirus software temporarily, or performing a clean boot.
MSI error 2502 is a common issue that occurs during the installation or uninstallation of software in Windows. It generally arises due to corrupt or incomplete installation files, outdated drivers, or conflicts with other software. To fix the problem, you can try several solutions such as running the installer as an administrator, clearing temporary files, disabling antivirus software temporarily, updating drivers and operating system, and repairing registry entries.
Additionally, you can also use third-party tools like CCleaner to clean up your system and remove any unwanted files that may be causing the error. By following these steps carefully, you can resolve MSI error 2502 and ensure smooth software installations on your Windows computer.
Check the user permissions of C:\Windows\Temp and ensure the current user has full access to that folder as well as TrustedInstaller and Administrative accounts on the network.
To prevent future occurrences of MSI error 2503 and 2502, it’s important to maintain a clean and organized computer system. Regularly cleaning up temporary files, removing unnecessary programs, and updating drivers can help prevent errors from occurring.
It’s also essential to be cautious when installing new software or updates. Make sure you’re downloading the software from a trusted source and that your computer meets the program’s system requirements.
Another way to prevent errors is to run regular scans for viruses and malware. Malicious software can cause various issues with your computer, including MSI errors.
By following these preventative measures, you can reduce the likelihood of experiencing MSI error 2503 and 2502 in the future.
Flipper Zero is a revolutionary hacking tool that has been making waves in the security industry since its launch. This compact device is designed to help security professionals and enthusiasts explore, monitor and control electronic devices with ease. The Flipper Zero comes with a range of features, including RFID, infrared, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and an OLED screen that makes it easy to navigate through menus and perform tasks.
With its open-source architecture and user-friendly interface, the Flipper Zero can be customized to suit individual needs and preferences. However, as with any powerful tool, there are also risks associated with the Flipper Zero. In this article, we will explore some of the potential dangers posed by blackhat hacking tools like the Flipper Zero and how users can protect themselves from these threats.
As technology continues to advance, black hat hackers are vigilant in finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to systems. These hackers use various tools and techniques to achieve their malicious goals, such as malware, phishing attacks, and social engineering tactics. One of the most dangerous tools that black hat hackers have at their disposal is ransomware. This type of malware encrypts a victim’s files and demands for payment in exchange for the decryption key.
Another tool that has become increasingly popular among hackers is the botnet, which allows them to take control of multiple devices remotely and use them for DDoS attacks or other nefarious purposes. As we move towards an increasingly connected world with more devices being added to the Internet of Things (IoT), it is important to be aware of the potential dangers posed by blackhat hackers and their tools.
The emergence of Flipper Zero, a new black hat hacking tool, is a significant threat to cybersecurity. With its ability to exploit vulnerabilities in electronic devices, Flipper Zero can access sensitive information and compromise security systems. The FLipper Zero’s compact size and portability make it an ideal and very accessible tool for cybercriminals to carry out attacks remotely. Moreover, its user-friendly interface allows even novice hackers to use it with ease.
Flipper Zero’s ability to bypass traditional security measures like firewalls and antivirus software poses a serious challenge to cybersecurity experts. The increasing popularity of this tool among the hacker community makes it crucial for organizations and individuals alike to be aware of its existence and take necessary precautions against potential attacks. As technology continues to advance, the threat posed by tools like Flipper Zero will only grow stronger, highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures that can keep up with these evolving threats.
As new hacking tools like Flipper Zero emerge, it is important to take proactive measures to identify and protect your personal and business data. First, ensure that all your devices are updated with the latest, firmware, security patches, and software updates. Secondly, always use strong and unique passwords for all your accounts, and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks or unsecured websites that may leave you vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Additionally, invest in reputable EDR Security software that can detect and prevent malicious activities on your entire business network and devices. Finally, be vigilant of phishing scams and suspicious emails or messages from unknown sources. Remember that prevention is always better than cure when it comes to cybersecurity threats posed by new hacking tools like Flipper Zero. Stay informed and take action to protect yourself from potential risks.
CEO fraud, also known as “Business Email Compromise,” is a type of cybercrime where a hacker impersonates a CEO or other high-ranking executive within an organization to trick employees into transferring money or sensitive information. The attacker usually gains access to the company’s email system and sends an urgent request to an employee, posing as the CEO, asking them to transfer funds or provide confidential data.
The email may seem legitimate since it appears to come from a trusted source and often contains details about ongoing business deals. Once the employee complies with the request, the hacker can steal the money or use the stolen information for further attacks. To prevent CEO fraud, companies should implement strict email security protocols and educate employees on how to identify suspicious requests.
The rise of CEO fraud has become a major concern for businesses of all sizes. This type of cyber attack involves criminals impersonating high-level executives, often through phishing emails, to trick employees into transferring funds or sensitive information. The impact can be devastating, resulting in significant financial losses and damage to a company’s reputation. In fact, the FBI reported that CEO fraud scams have resulted in over $26 billion in global losses since 2016.
Despite increased awareness and training efforts, these attacks continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, making it crucial for businesses to implement strong cybersecurity measures and protocols to protect against CEO fraud.
One strategy for preventing CEO fraud attacks is to implement strict email security measures. This includes using email authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify the sender’s identity and prevent spoofing. Additionally, companies can train employees on how to identify phishing emails and avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments.
Another effective approach is to establish a multi-factor authentication system for sensitive transactions such as wire transfers or vendor payments. This requires additional verification beyond just a username and password, making it harder for fraudsters to gain access.
Regularly reviewing and updating internal controls can also help prevent CEO fraud attacks. This includes regularly reviewing vendor payment processes, conducting background checks on new hires with access to financial information, and limiting access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel.
CEO fraud is a type of cybercrime where criminals impersonate senior executives to deceive employees into transferring money or sensitive information. This scam is becoming increasingly sophisticated, and it often targets employees who are not trained in cybersecurity best practices. To prevent CEO fraud, companies must prioritize employee training and awareness programs. Employees need to understand the risks of opening suspicious emails, clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
They also need to know how to verify requests for sensitive information or financial transactions, especially if they come from senior executives. By investing in employee training and awareness, companies can empower their workforce to identify and report potential threats, ultimately reducing the risk of CEO fraud attacks.
The future of CEO fraud remains uncertain, but one thing is clear: companies must remain vigilant. With the rise of sophisticated cybercriminals and the continued use of social engineering tactics, it is likely that CEO fraud will continue to be a significant threat to businesses. As technology advances, scammers and malicious threat actors are finding new ways to deceive employees and gain access to sensitive information.
It is important for businesses of all sizes to implement strong cybersecurity protocols, provide ongoing training for employees, and have a plan in place for responding to potential CEO fraud attacks. Failure to do so could result in, life-changing, devastating financial losses and cause extreme damage to a company’s reputation. The need for continued vigilance cannot be overstated when it comes to protecting against CEO fraud.
The MITRE ATT&CK Framework is a comprehensive knowledge base that outlines the various tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by cyber attackers to infiltrate networks and compromise data. It was developed by MITRE Corporation, a non-profit organization that works in the field of cybersecurity research and development. The framework provides a standardized language for describing cyber-attacks and helps organizations to better understand the various stages involved in an attack.
This knowledge can be used to improve security measures and develop more effective incident response plans. The framework is organized into two main components: tactics and techniques. Tactics refer to the overarching goals of an attacker, such as gaining access or maintaining persistence within a network. Techniques are the specific methods used to achieve these goals, such as exploiting vulnerabilities or using social engineering tactics.
The MITRE ATT&CK Framework has become widely adopted across industries as a key tool for improving cybersecurity posture.
The need for an attack classification system arises from the increasing complexity and diversity of cyber threats. As organizations rely more on technology, they become more vulnerable to attacks from hackers who are constantly developing new methods to compromise networks and systems. An attack classification system provides a standardized framework for identifying and categorizing different types of cyber-attacks based on their tactics, techniques, and procedures.
This allows organizations to better understand the nature of the threat and take appropriate measures to prevent or mitigate its impact. Additionally, having a common language for describing attacks enables better communication between security teams, vendors, and other stakeholders in the cybersecurity ecosystem. Mitre ATT&CK is one such attack classification system that has gained popularity due to its comprehensive coverage of various stages of a cyber attack.
With the ever-evolving threat landscape, an effective attack classification system is crucial for organizations to stay ahead of potential attackers.
The development of attack classifications has been a crucial aspect of the field of cybersecurity. The initial classification systems were mainly based on the type of vulnerability exploited by attackers, such as buffer overflow or SQL injection attacks. However, as cyber threats grew more complex and sophisticated, these classifications became inadequate. To address this issue, the MITRE Corporation introduced the Adversarial Tactics, Techniques & Common Knowledge (ATT&CK) framework in 2013.
This framework provides a comprehensive classification system for cyber threats based on the tactics and techniques employed by attackers during different stages of an attack. The ATT&CK matrix is continually updated to reflect emerging trends in cyber attacks and includes categories such as initial access, execution, persistence, defense evasion, credential access, discovery, lateral movement, collection, exfiltration, and impact. The ATT&CK framework has revolutionized how organizations approach cybersecurity by providing a common language for describing threat activities.
Attack classifications refer to the different categories that cyber attacks can be grouped into based on their characteristics and methods of execution. The main types of attack classifications include passive attacks, active attacks, insider attacks, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and social engineering attacks. Passive attacks involve monitoring or eavesdropping network traffic to obtain sensitive information without altering it. Active attacks, on the other hand, involve manipulating or altering data in transit or at rest for malicious purposes.
Insider attacks are carried out by individuals with authorized access to a system who misuse their privileges for personal gain or revenge. DDoS attacks flood a system with traffic from multiple sources to overload and disrupt its services. Social engineering attacks exploit human behavior and psychology to manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. Understanding these attack classifications is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect against them.
The MITRE ATT&CK Matrix is a comprehensive framework that categorizes and describes various attack tactics and techniques used by threat actors. It is widely considered as a valuable tool for cybersecurity professionals to understand the structure and function of cyberattacks. The matrix consists of two main components, tactics and techniques. Tactics represent the overarching goals of an attacker, while techniques are the specific methods used to achieve those goals.
The matrix has several classifications, including pre-attack, initial access, execution, persistence, defense evasion, credential access, discovery, lateral movement, collection, exfiltration, and command and control. By categorizing attacks in this way, security analysts can identify potential vulnerabilities in their systems and develop appropriate defenses against them. Understanding the structure and function of MITRE ATT&CK Matrix can help organizations improve their security posture by identifying gaps in their defenses.
Mapping attacks to the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix is a crucial step in understanding and mitigating cybersecurity threats. The MITRE ATT&CK framework provides a comprehensive list of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) that attackers may use during an attack. By mapping an attack to the matrix, analysts can identify the specific TTPs used by the attacker and create effective countermeasures to prevent future attacks.
The process involves breaking down an attack into its component parts and identifying which TTPs were employed at each stage. This requires a deep understanding of both the attack methodology and the organization’s network architecture. The result is a detailed report that outlines all aspects of the attack, including how it was executed, what data was targeted, and which systems were compromised.
Mapping attacks to the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix enables organizations to proactively defend against future attacks by creating tailored defense strategies based on identified TTPs.
The MITRE ATT&CK framework has become a critical tool for organizations looking to strengthen their cybersecurity defense strategies. The framework provides a comprehensive view of the various tactics and techniques used by attackers, enabling organizations to better understand and prepare for potential threats. By mapping out the different stages of an attack, the framework also helps organizations identify potential vulnerabilities in their systems and develop more effective response plans.
One of the key benefits of using the MITRE ATT&CK framework is its ability to provide a standardized language for discussing cybersecurity threats across teams. This common language allows security analysts, incident responders, and other stakeholders to work together more effectively, streamlining communication and collaboration during an attack. Additionally, as attackers continue to evolve their tactics, the MITRE ATT&CK framework provides a living document that can be updated with new threat intelligence and best practices over time.