Executive assistants are the strategic hub of any organization, managing schedules, communications, and sensitive information with unparalleled skill.
This article explores how LayerLogix’s IT solutions empower executive assistants to enhance productivity, strengthen security, and navigate the complexities of modern technology, transforming them into even more valuable assets for their organizations.
The demands on EAs are constantly evolving, requiring not only exceptional organizational skills but also a deep understanding of technology and its impact on productivity and security.
In fact, executive assistants are rapidly adopting technology, with an estimated 27% of medium-sized businesses and 35% of large companies utilizing virtual executive assistants.
This trend is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing reliance on technology in the workplace.
LayerLogix recognizes these evolving demands and acts as a strategic partner, empowering EAs with tailored technology solutions that enhance productivity, strengthen security, and simplify IT complexities.
That’s why LayerLogix helps you navigate this complex landscape by providing:
Our approach is rooted in understanding your unique needs.
We work closely with you to assess your current IT landscape, identify pain points, and develop customized solutions that align with your specific requirements and business objectives.
For practical tips and essential tech tools for EAs, explore our articles “Top Tech Productivity Hacks for Busy Executive Assistants” and “Top Cybersecurity Apps and Tools Every Executive Assistant Should Use”
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into LayerLogix’s specific service offerings and demonstrate how we can empower you to navigate the complexities of technology, enhance your productivity, and strengthen your cybersecurity posture.
LayerLogix’s IT solutions are designed to be the former, transforming your workflow into a well-oiled, productivity-boosting machine.
And as we all know, one of the biggest productivity killers is repetitive, manual tasks.
Think about how much time you spend each day on email management, scheduling appointments, or generating reports. LayerLogix can help you automate these tedious processes, freeing up your valuable time for more strategic activities.
We implement and integrate tools that streamline workflows, allowing you to accomplish more in less time, with greater accuracy and reduced stress.
Automation tools for administrative tasks can save significant amounts of time, potentially freeing up hours or even entire days per week, depending on the volume and complexity of the tasks automated.
Effective communication and collaboration are essential for any successful EA.
We provide and support communication platforms that enhance teamwork and streamline information flow, whether it’s through instant messaging, video conferencing, or shared project management tools.
A slow or unreliable network can bring your productivity to a screeching halt.
LayerLogix designs and manages robust IT infrastructures that ensure seamless connectivity, fast data access, and optimal performance of your applications and devices.
This eliminates frustrating tech issues and allows you to focus on your work, not your technology.
And when technical issues do arise, our 24/7 IT support team is there to provide prompt and reliable assistance. We understand that every minute counts in your busy schedule, and we’re committed to minimizing downtime and maximizing your productivity.
A 2024 report revealed that a staggering 76% of businesses were targeted by smishing attacks in just one year, highlighting the increasing vulnerability of organizations to cybercrime.
Furthermore, over 75% of targeted cyberattacks originate with a simple email, underscoring the importance of robust email security and employee awareness.
LayerLogix understands these evolving challenges and offers a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity solutions tailored to the needs of executive assistants:
We go beyond basic antivirus software, implementing and managing advanced threat detection and prevention systems that identify and neutralize cyber threats in real time.
Our solutions protect your devices, networks, and data from malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and other malicious activities, ensuring your organization’s sensitive information remains safe.
We encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest, adding an extra layer of security and making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals.
We also implement strict access controls, limiting access to confidential information based on roles and responsibilities, and minimizing the risk of insider threats or accidental data leaks.
A study by Varonis found that, on average, every employee has access to 11 million files, with 17% of all sensitive files accessible to all employees.
This highlights the critical need for granular access controls and data protection measures.
Because email is a primary target for cyberattacks, we provide robust email security solutions that include anti-phishing measures, spam filtering, and email encryption, protecting your inbox and your organization from email-borne threats.
A 2020 Internet Crime Report revealed that losses due to phishing and related scams amounted to over $54.2 million in 2019, underscoring the financial impact of these attacks.
We don’t just react to threats; we anticipate them.
Our team conducts regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in your systems before attackers can exploit them.
We then work with you to implement proactive measures to mitigate these risks and strengthen your overall security posture.
Since human error is a significant factor in many cyberattacks, we empower your team with the knowledge and skills to recognize and avoid threats.
Our customized training programs cover topics like phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and password management best practices, ensuring your team is your first line of defense against cyber threats.
A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the damage and ensuring business continuity in the event of a cyberattack.
We help you develop and test comprehensive incident response plans, so you’re prepared to handle a security incident effectively and recover quickly.
Shockingly, more than 77% of organizations don’t have an incident response plan in place.
The cloud computing market is projected to reach a staggering $947.3 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.3%.
This widespread adoption is driven by the cloud’s ability to empower businesses with enhanced efficiency, accessibility, and cost savings.
For executive assistants, cloud solutions provide a powerful suite of tools and resources to streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and boost productivity.
LayerLogix understands the transformative potential of the cloud and offers tailored solutions designed to empower executive assistants:
Access your essential tools from anywhere, anytime.
Cloud-based productivity suites, like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365, provide a comprehensive range of applications for document collaboration, file sharing, email management, and video conferencing, all accessible from any device with an internet connection.
This flexibility and accessibility are crucial for today’s increasingly mobile and distributed workforce.
Streamline collaboration and ensure everyone is on the same page.
This eliminates the need for emailing attachments back and forth and ensures everyone is working with the most up-to-date versions of documents.
The number of people using personal clouds has more than doubled since 2014, reaching an estimated 2.3 billion users today, demonstrating the widespread familiarity and adoption of these tools.
Modernize your communication system and enhance flexibility.
Cloud-based phone systems (PBX) offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, allowing executive assistants to manage calls, voicemails, and communications seamlessly, regardless of location.
This is particularly beneficial for remote or hybrid work environments, providing a unified communication system that enhances accessibility and collaboration.
Offload the burden of IT management and free up valuable resources.
Migrating IT workloads to the cloud reduces the demands on in-house IT staff, allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
LayerLogix’s expertise in cloud workload migration ensures a smooth and secure transition, minimizing disruption and maximizing the benefits of cloud computing.
Strengthen your security posture and protect sensitive data.
LayerLogix leverages these inherent security features and implements additional security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and access controls, to safeguard your data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
LayerLogix’s cloud solutions are tailored to your specific needs.
We’ll help you navigate the cloud landscape, choose the right solutions for your business, and manage your cloud environment effectively, ensuring security, scalability, and optimal performance.
A slow network, a malfunctioning computer, a software glitch – these seemingly minor issues can derail your workflow, disrupt your schedule, and impact your ability to support your executive effectively.
That’s why LayerLogix goes beyond simply providing tools; we offer a proactive approach to IT support that anticipates and addresses potential problems before they impact your productivity.
Proactive IT management is the key to a stable and efficient IT environment.
It involves continuous monitoring of systems, early detection of potential issues, and predictive risk mitigation.
This approach not only reduces downtime but also ensures that your technology is always running smoothly, allowing you to focus on your core responsibilities without the constant distraction of technical problems.
By outsourcing your IT support to LayerLogix, you gain access to specialized expertise without the need for a large, expensive in-house IT team.
This not only reduces costs but also ensures you have the right skills and knowledge to navigate the complexities of today’s technology landscape.
The IT consulting industry is booming, with revenue projected to reach $27.22 billion in 2024, reflecting the increasing demand for expert IT guidance and support.
Every executive assistant plays a crucial role in managing sensitive information and ensuring the smooth operation of their executive’s digital life.
We could say they’re gatekeepers of information, entrusted with sensitive data, confidential communications, and the smooth operation of their executives’ digital lives.
However this isn’t just about protecting your company’s data; it’s about protecting your productivity, reputation, and peace of mind.
A well-equipped cybersecurity toolkit empowers executive assistants to navigate the digital landscape safely and efficiently, minimizing risks and maximizing their effectiveness.
Executive assistants are entrusted with a unique blend of responsibilities: managing schedules, coordinating communication, and handling sensitive information.
This access to confidential data makes cybersecurity a critical concern for EAs.
Fortunately, a range of powerful tools and apps can help safeguard your information and streamline your workflow, allowing you to focus on your core tasks with confidence.
Let’s face it, passwords are a pain.
We all have dozens, if not hundreds, of them, and trying to remember them all is a recipe for disaster.
Weak passwords, reused passwords, and scribbled-down passwords on sticky notes are all vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
In fact, 57% of users reported having a password written down on a sticky note, and a shocking 44% of users reported recycling passwords across personal and business-related accounts.
Password management tools offer a secure and efficient solution.
These tools generate strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts, store them securely in an encrypted vault, and automatically fill them in when you need them.
This not only enhances security but also saves you time and frustration, eliminating the need to remember or reset passwords constantly.
Here are a few top-rated password management tools:
| Password Manager | Biggest Feature |
| Bitwarden | Open-source and highly transparent. This appeals to users who prioritize security and want to be able to audit the code. It also offers a generous free plan. |
| LastPass | Widely known and trusted, with a long history in the industry. This provides security and reliability for users who prefer a well-established solution. |
| 1Password | Focus on user experience and ease of use. This makes it a good choice for users new to password managers or who prefer a more intuitive interface. |
| Dashlane | Premium experience with advanced features. This appeals to users willing to pay for extra security and convenience. |
Choosing the right password manager depends on your specific needs and preferences, but the key is to use something to protect your passwords and enhance your cybersecurity posture.
Email is the lifeblood of modern business, but it’s also a prime target for cybercriminals.
Phishing scams, malware attacks, and data breaches can all originate from a single malicious email, making inbox security a top priority for executive assistants.
Fortunately, a range of powerful tools and apps can help you shield your inbox from these threats.
Services like Mimecast offer comprehensive email security solutions that go beyond basic spam filters.
They scan incoming and outgoing emails for malware, phishing attempts, and other malicious content, blocking threats before they reach your inbox.
Mimecast also provides email archiving, backup, and recovery services, ensuring business continuity in case of a disruption.
Some email clients, like Canary Mail, prioritize security with features such as end-to-end encryption, phishing protection, and read receipts.
These clients offer a more secure alternative to traditional email platforms, especially for highly sensitive communications.
Browser extensions like Netcraft and PhishDetector can help you identify phishing websites and emails, providing an extra layer of protection against these deceptive attacks.
These extensions analyze website URLs, email headers, and other indicators to identify potential phishing attempts, alerting you to potential risks.
By combining these email security apps and tools, executive assistants can create a robust defense against email-borne threats, protecting their inboxes, their data, and their organizations.
Executive assistants are increasingly mobile, working from laptops, smartphones, and tablets both in the office and on the go.
This mobility, while offering flexibility and convenience, also expands the potential attack surface for cyber threats. Securing your devices is paramount to protecting sensitive data and maintaining productivity, wherever you’re working.
Traditional antivirus software is no longer enough.
Modern endpoint protection platforms, like CrowdStrike Falcon and Intercept X Advanced, offer comprehensive protection against malware, ransomware, and other sophisticated attacks.
They use advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect and respond to threats in real time.
These tools go beyond simply scanning for known viruses; they actively monitor device behavior, identify anomalies, and block malicious activity before it can cause damage.
Encrypting your device’s hard drive adds another layer of protection, ensuring that your data remains inaccessible even if your device is lost or stolen. Tools like VeraCrypt offer robust encryption capabilities, safeguarding your files and folders from unauthorized access.
Let’s not forget that 73% of companies in North America use browsers that are out of date, leaving them vulnerable to attacks.
By implementing these device security measures, executive assistants can protect their data, maintain their productivity, and ensure the security of their organization’s information, regardless of where they’re working.
LayerLogix can help you assess your device security needs and implement the right solutions to safeguard your business.
Data protection and privacy are paramount in today’s digital landscape, especially for executive assistants handling sensitive business information.
Fortunately, a range of tools and apps can help you safeguard confidential data and maintain compliance with privacy regulations.
DLP tools, like Forcepoint, monitor and control the movement of sensitive data within your organization, preventing accidental or intentional leaks.
They can identify and block the sharing of confidential information via email, cloud storage, or other channels, ensuring your organization’s data remains protected.
Encryption scrambles data into an unreadable format, making it useless to anyone who doesn’t have the decryption key. For example, tools like 7-Zip, a free and open-source file archiver, offer strong encryption capabilities for compressing and protecting files.
When sharing files with colleagues, clients, or partners, use secure file-sharing platforms that offer encryption and access controls.
Consider tools like ShareFile or Tresorit, which provide secure file storage, sharing, and collaboration features.
On the other hand, avoid sending sensitive information via unencrypted email attachments, which are vulnerable to interception.
Consider using privacy-focused browsers like Brave or Firefox with privacy-enhancing extensions like Privacy Badger or HTTPS Everywhere.
These tools can block trackers, prevent websites from collecting your browsing data, and ensure you’re always using a secure HTTPS connection.
Tools like OneTrust and BigID help organizations manage data privacy, comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, and build trust with customers.
These platforms offer features such as data discovery, consent management, and data subject rights fulfillment.
Executive assistants are on the front lines of business communication, often handling sensitive information and managing access to critical systems.
This makes them prime targets for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to valuable data.
While technology tools play a crucial role in cybersecurity, adopting best practices and cultivating a security-conscious mindset are equally important.
Here are some essential cybersecurity best practices for executive assistants and other C-suite professionals:
By adopting these cybersecurity best practices, executive assistants can play a vital role in protecting their organizations from cyber threats.
Remember, cybersecurity is everyone’s responsibility, and a proactive and vigilant approach is essential for staying safe in the digital age.
Cybercriminals are constantly devising new tactics to create and send dangerous email attachments, using them as a gateway to unleash malware, viruses, and other malicious software.
To safeguard ourselves and our systems, it’s essential to understand why some email attachments are dangerous, which types pose a high risk, and how to spot them effectively.
In this article, we will delve into the world of dangerous email attachments and equip you with the knowledge to protect yourself.
Email attachments pose a threat primarily because they can contain malicious files or code that can exploit vulnerabilities in our systems.
Cybercriminals leverage social engineering techniques to trick recipients into opening these attachments, often disguising them as harmless or enticing files.
Once opened, these attachments can unleash malware, viruses, ransomware, or other harmful software, leading to data breaches, system damage, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Among the high-risk email attachments, executables (.exe) are particularly dangerous.
These files have the capability to run codes that can modify a computer system.
Cybercriminals often disguise them with innocent-sounding names to deceive recipients into opening them.
Executable files can be vehicles for ransomware, encrypting files and demanding payment for decryption, or they can serve as carriers for other malicious software.
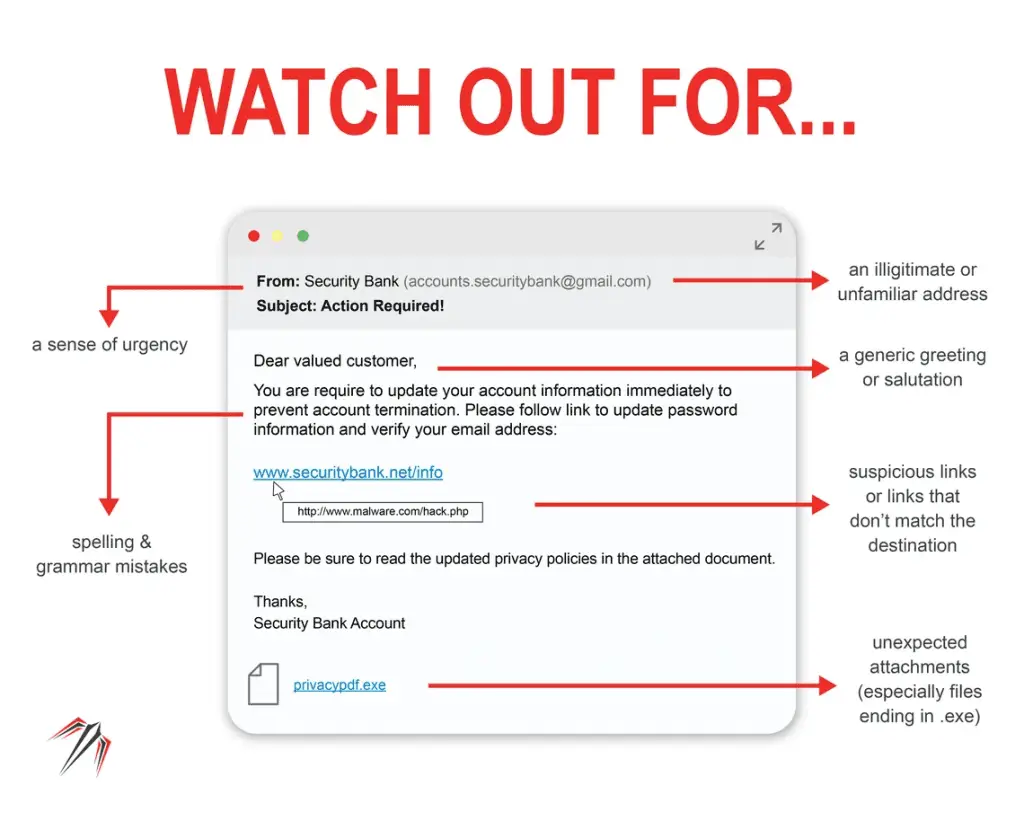
Such as .js, .vbs, .php, or .asp files, are another high-risk attachment type. While not inherently malicious, cybercriminals utilize scripts to install malware on victims’ computers.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in software or manipulating user interactions, malicious scripts can execute harmful commands or actions, compromising system integrity and privacy.
In various formats (.doc, .xls, .ppt, .pdf) also pose a significant risk. Cybercriminals inject malicious code into seemingly harmless documents, such as Microsoft Office files or PDFs, and prompt users to enable macros or click on phishing links.
Enabling macros or interacting with these documents can lead to the activation of malware, unauthorized access, or theft of login credentials.

Archive files, including .zip, .rar, or .7z, are commonly used by cybercriminals to conceal malware. These compressed files provide an effective means of delivering malicious executables, scripts, or infected documents.
By enticing recipients with intriguing filenames or exploiting their curiosity, cybercriminals trick users into extracting the contents of the archive, inadvertently activating the hidden malware.
Disk image files, such as .iso, .img, or .dmg, are particularly risky, especially for macOS users. These files can contain executables, scripts, or documents that can compromise system security.
Cybercriminals often bundle disk images with seemingly harmless files, using social engineering to entice users into executing the installer and unknowingly installing malware.

Not all email attachments are dangerous, but it’s essential to exercise caution and verify the authenticity of the attachment and the sender before opening it.
Cybercriminals often use social engineering tactics to trick users into opening malicious attachments, so it’s crucial to be vigilant.
If you receive a suspicious email attachment, it’s best to avoid opening it.
Delete the email and attachment immediately.
If the email appears to be from someone you know, contact them through another communication channel to verify the attachment’s legitimacy.
While email attachments from trusted sources are generally safer, it’s still essential to exercise caution.
Cybercriminals can compromise email accounts or use spoofing techniques to make an email appear legitimate.
Always verify the sender and the content of the attachment before opening it.
Antivirus software is an essential layer of protection, but it’s not foolproof.
Cybercriminals constantly develop new techniques to evade detection.
Therefore, it’s crucial to adopt a multi-layered security approach, which includes being vigilant, staying informed, and following best practices for email safety.
To help mitigate the risks of cyber threats targeting unsuspecting users every day through email, many organizations rely on Secure Email Gateways (SEG), which are designed to block incoming threats and filter out unwanted or malicious messages.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at some of the leading SEG solutions on the market, including their key features and benefits, to help you choose the best one for your business.
Secure email gateways (SEGs) are an essential tool for email security solutions, as they provide protection against email-borne threats. However, the effectiveness of SEGs has been limited in recent years.
Many SEGs have failed to keep up with the ever-changing threat landscape, which has led to an increase in social engineering attacks. In addition, the design of SEGs makes them less suitable for protecting cloud-based email solutions.
One limitation of SEGs is that they rely heavily on a set of predefined rules and policies, which may not be enough to detect all types of email threats.
Sophisticated phishing attacks that use new and creative techniques can often pass through these rules and policies, which makes it difficult for SEGs to protect against them.
Another limitation is that SEGs are less effective at protecting cloud-based email solutions such as Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace. This is because the design of SEGs is based on inspecting emails inline, which means that they need to sit in line on the path of emails from the public internet to the corporate email server.
This design makes them less effective at protecting cloud-based email solutions, which often require an API-based approach.
To overcome these limitations, organizations need to implement more advanced email security solutions. One such solution is the cloud-native email security, which uses an API-based approach to protect cloud-based email solutions.
Cloud-native email security solutions can analyze data from multiple sources, including email, identity, and web browsing behavior, to identify threats that traditional SEGs cannot.
Another solution is to use machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to improve the effectiveness of SEGs. Machine learning and AI can help identify new and emerging threats that SEGs might not have seen before, allowing organizations to quickly adapt and update their security measures.
In this article, we will explore the best secure email gateways for businesses, both small and large, for the year 2023.
Email is a ubiquitous communication tool used by individuals and businesses alike. Unfortunately, it’s also a prime target for cybercriminals, so it’s crucial to have the best email-scanning software in place to protect against these threats.
In this article, we’ll take a look at some of the top email scanners available in 2023. From Norton 360’s comprehensive suite of anti-virus tools to open-source solutions like MailScanner, there’s no shortage of options to choose from.
Whether you’re a small business owner or a tech-savvy individual, you’re sure to find an email scanner that meets your needs.
Email scanning is an automated process that checks every email message for viruses, malware, and spam. It also inspects links and attachments for possible malicious attacks and looks for signs of email spoofing commonly used in impersonation attacks.
This technology is deployed both at the email perimeter and inside it, using the latest threat intelligence and corporate content control and DLP policies to block, quarantine, or flag emails that may contain any potential threats.
These solutions can use various techniques to identify malicious content, such as scanning for signatures of known malware variants and using AI and ML to detect novel threats or potential social engineering attacks.
But what are the exact malware and other threats that email scanners can detect?
Email scanning solutions can help identify and block various types of email threats. These solutions include:
Unfortunately, with the convenience of email comes the constant threat of cyber-attacks through malicious emails. That’s where email scanning software comes in.
Here are the top email scanners for 2023:
First on the list is Norton 360, the highly-rated anti-virus utility. Its Premium subscription offers a complete package of anti-spyware, antivirus, malware, and ransomware protection, including a separate email scanner that checks incoming attachments and hyperlinks for viruses, spyware, and malware.
Next is AVG Internet Security, which offers a freeware version and a premium version with a limited email scanner that can block suspicious email attachments, spam, and phishing emails. The software also includes various email configuration options and advanced features such as AI detection and behavior shields.
For those looking for an all-in-one solution, Mimecast provides email security, continuity, archiving, compliance, and backup and recovery, all in a cloud-based subscription service. Its email scanning system can scan all inbound, outbound, and internal emails for threats to the organization.
CheckPoint/Avanan also offers a comprehensive email security platform that can replace SEG and non-SEG for inbox security, with the recent acquisition of Avanan by Check Point making it a stronger WFH security contender.
Barracuda Email Threat Scanner is another powerful email scanner, with an artificial intelligence platform that understands the sender’s intent to detect social engineering attacks.
SpamTitan is a double anti-virus email scanner with a 99.99% spam catch rate, while MailScanner is an open-source email security system designed for Linux-based email gateways, used by top government departments, corporations, and educational institutions worldwide.
With the constant threat of cyber attacks, it’s essential to have email scanning software that can keep you protected.
Choose the best email scanner for your needs and keep your emails safe and secure.
Email has become a crucial part of our communication in today’s digital world, so to send secure email becomes a top business priority. It is fast, convenient, and widely accessible. However, sending sensitive information via email can be risky if it is not protected properly.
While Gmail and Outlook are popular email providers, many users are unaware of the options available to them for sending secure emails and attachments.
The truth is that not all emails are created equal in terms of security.
If you’re sending casual emails with pictures of your latest vacation, you’re probably not too concerned about security. But if you’re a journalist, a business owner, or someone who frequently sends sensitive documents, it’s essential to know how to send secure or encrypted emails.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of sending secure emails and attached documents via Gmail and Outlook. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, our step-by-step instructions will help you send your emails with confidence. Write down to send secure email as one of your pressing business goals of this year.
Gmail is a popular email service that uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) as a standard for keeping emails secure during delivery. However, TLS doesn’t provide the added security of keeping emails safe after they’ve been delivered.
Fortunately, Gmail offers a solution for this problem with its Confidential Mode, available in both free and paid Gmail accounts. Here are the step-by-step instructions for using Gmail Confidential Mode in a free account:
If you want to password-protect MS Office Suite files, such as Word, Excel, or PowerPoint, you can use the Encrypt with Password feature. This option can usually be found under the
Prepare the document for distribution function, but the way to access it depends on the version of the software you are using. Keep in mind that even though MS Suite has encryption, the decryption key is reduced to a simple user-picked password, which makes the document more vulnerable to hacking.
As for sending secure email attachments and documents through Gmail, Google Docs is an option. However, Google Docs items cannot be password-protected as your account login is considered a security clearance.
Therefore, sending a page link via email may not be the best idea. While there are third-party add-ons available to enable password protection for Google Docs, their reliability may vary.
Microsoft’s Outlook provides default encryption with TLS (Transport Layer Security), but it only works if the recipient’s service also supports it. Microsoft also has been caught working with US intelligence agencies, which raises privacy concerns.
If you want to send a more secure message in Outlook, you can enable enhanced encryption with Microsoft 365 Message Encryption (OME). However, this feature is only available with a premium account, such as Microsoft 365 Family or Microsoft 365 Personal, or an eligible enterprise account.
Once you’ve enabled OME, you can send emails and documents attached through the Outlook.com web or desktop app. The recipient can open the email using a Microsoft account, or Outlook can send them a passcode to open it.
If you have the Outlook desktop app, you can also enable S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) encryption, but it requires an eligible paid Microsoft account and technical skills to set up. S/MIME allows you to encrypt emails with user-specific keys so that only the intended recipients can decrypt them.
However, you cannot send a private message to anyone using a regular Outlook account or any other provider without S/MIME support. You also need to verify that they have S/MIME correctly set up before sending.
Sending documents securely through Outlook is also possible using password protection.
While digital document sharing is convenient, the safest way to send a document to someone is to hand it to them personally.
However, this is rarely an option, so encrypting documents with passwords or using OME or S/MIME encryption in Outlook provides a more secure option for sending sensitive information.